Category: Urinalysis
-

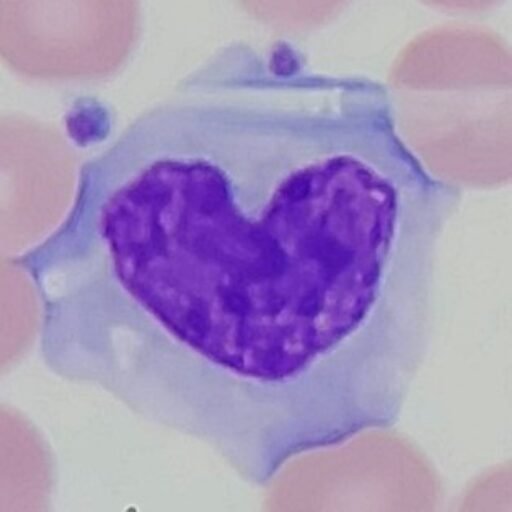
A urinalysis is ordered on a cloudy urine with a pH of 8.0. All other values on the urine chemistry are completely normal. Heating did nothing to clear the specimen. After spinning the urine sample, a layer of white sediment can be seen at the bottom. This sediment is filled with small granules. The brownian…
-

Practice grading different elements in a urine microscopic with positive crystals. Identify calcium phosphate crystals by pH and appearance.
-

Practice grading different elements in a urine microscopic with casts present. Use phase microscopy to identify hyaline casts.
-

Practice grading different elements in a urine microscopic with positive crystals. Identify both monohydrate and dihydrate forms
-

Practice grading different elements in a urine microscopic with positive crystals. Identify the thorny apple appearance of ammonium biurate.
-

Practice grading different elements in a urine microscopic with positive leukocytes, high turbidity, and bacteria present.
-
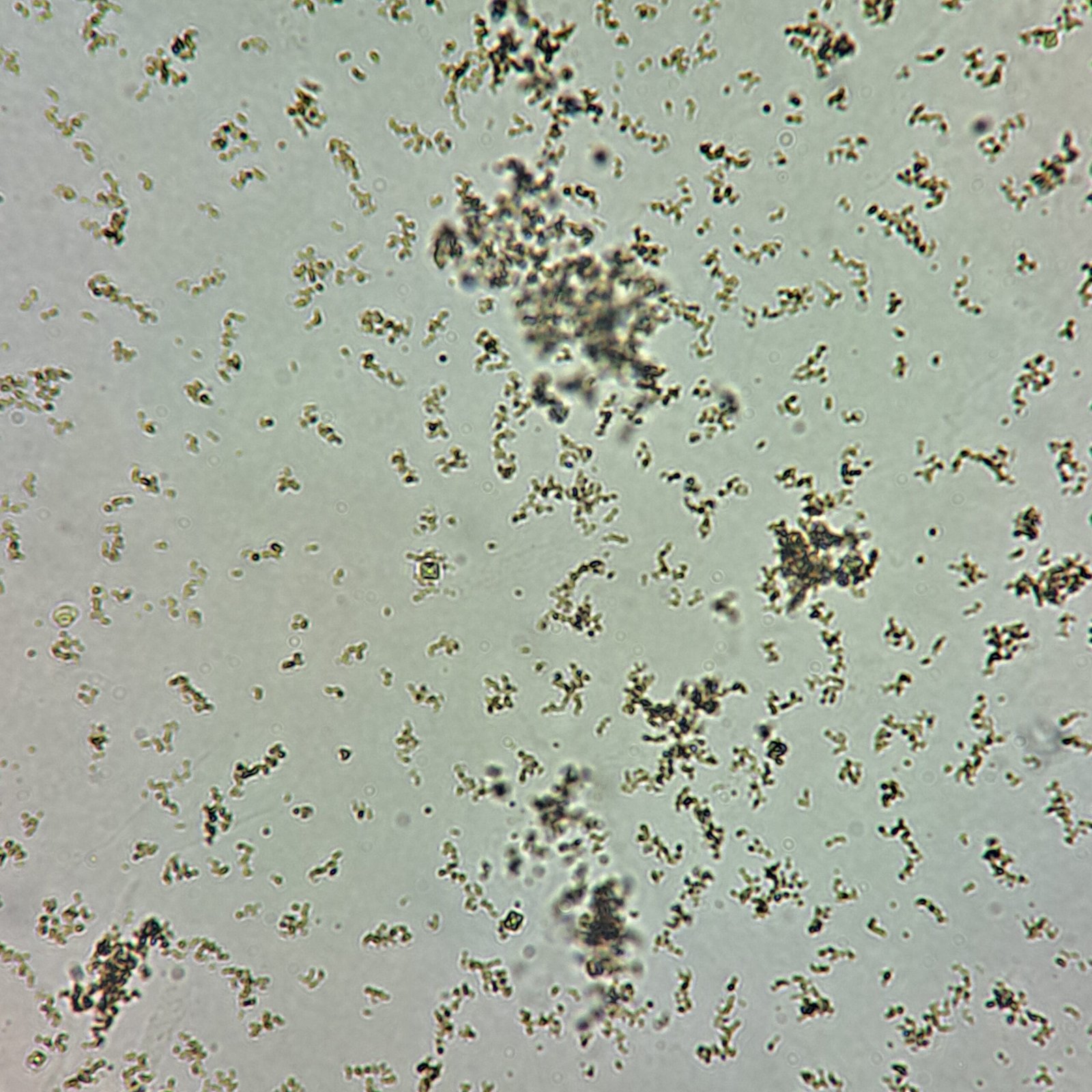
A urinalysis is added on to a refrigerated urine. The urine is extremely turbid with a pH of 5.5. Note that it is best practice to let the specimen come to room temp before testing. For the sake of example, this is not done. After spinning the urine sample, a layer of “brick dust” sediment…
-
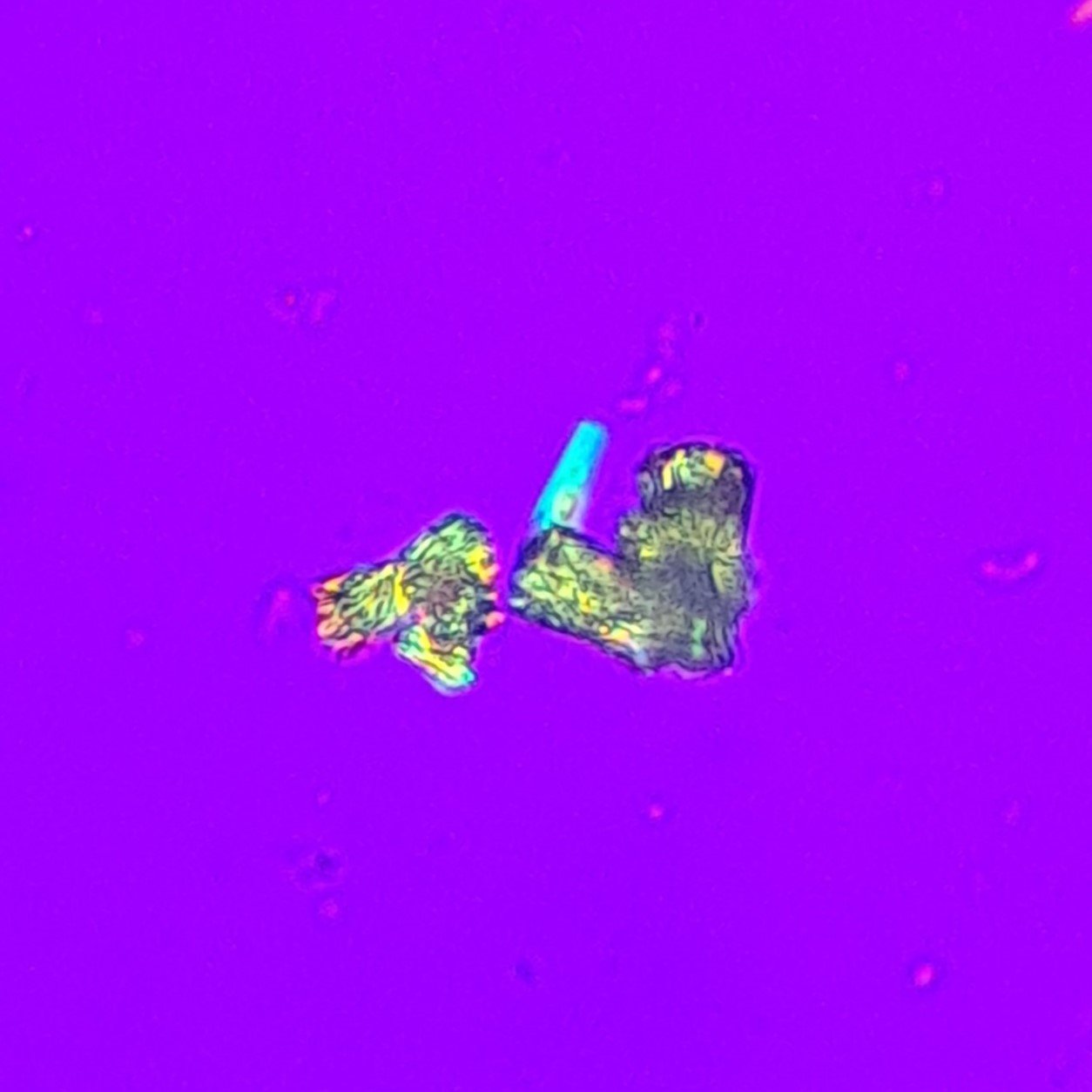

A patient had the following urine chemistries. Upon performing the microscopic Triple Phosphate crystals were easily identified with the alkaline pH. However, another type of crystal was noted that took the form of wheat sheaves and needles. Looking in the reference books, it looks like the crystals for medications such as ampicillin or indinavir. However,…