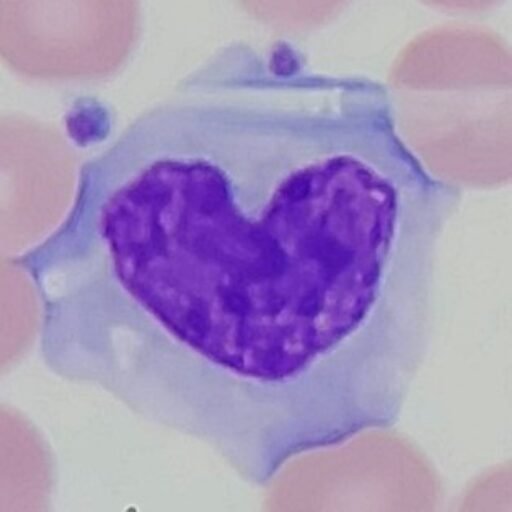
Potassium is the major intracellular cation, meaning it is a positively charged electrolyte found mainly inside the cells. It helps to maintain intracellular osmolality and regulate muscle excitability. It is commonly part of the basic metabolic panel. Normal range is 3.5 to 5.2 mmol/L for adults.
Hypokalemia (↓ K)
-Causes of Hypokalemia-
Decreased potassium levels in plasma is known as hypokalemia.
It is often caused by loss through the gastrointestinal tract via vomiting or diarrhea. The use of diuretics can also cause excess potassium to be excreted through urine. Similarly, Cushing syndrome causes increased aldosterone and increased excretion of potassium from the kidneys.
-Symptoms of Hypokalemia-
Since potassium has roles in muscle excitability, decreased plasma levels can cause muscle twitching or cramps as well as an irregular heartbeat.
Hyperkalemia (⭡ K)
-Causes of Hyperkalemia-
Increased potassium levels in plasma is known as hyperkalemia.
Kidney problems and dehydration can lead to elevated levels of potassium due reduced urinary excretion. Hyperkalemia can also be caused by potassium moving from tissues and cells into the extracellular fluid. This is seen with severe tissue injury (such as burns) and acidotic states (such as diabetic ketoacidosis).Excessive supplementation may be another cause for increased potassium levels.
-Symptoms of Hyperkalemia-
Since potassium has roles in muscle excitability, increased plasma levels can cause muscle weakness, numbness or tingling, as well as arrhythmia.
Spurious Results
_ Falsely Elevated _
(Pseudohyperkalemia)
Hemolysis: Since potassium levels are so much higher in cells than in plasma, hemolysis can cause falsely elevated results and is a cause for specimen rejection.
EDTA Contamination: Lavendar top tubes are commonly used in hematology to perform a complete blood count (CBC). To prevent clotting of the specimen, the tubes contain K2 or K3 EDTA anticoagulant. This additive contains potassium and chelates calcium, so contaminated samples will show significantly increased potassium and significantly decreased calcium. Contamination can occur from improper order of draw during blood collection or by pouring blood from the lavender top tube into another tube.
IV Fluid Contamination: If potassium is being administered intravenously and the blood is drawn from the same line without proper flushing, potassium may be falsely elevated.
Thrombocytosis: Potassium is released from platelets during clotting. In thrombotic conditions, the amount of potassium released during this process may cause potassium to be falsely elevated in serum samples. In this case, it is recommended to use plasma.
Extreme Leukocytosis: In cases of leukemia where the white count is markedly elevated (>100×10^9/L), the potassium released when white cells lyse can be enough to cause pseudohyperkalemia. Avoiding the use of pneumatic tube systems for transport and using serum samples instead of plasma can help mitigate this white cell lysis.
Clinical Examples
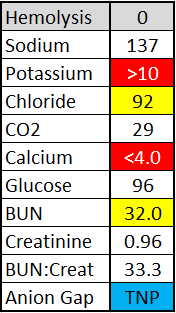
EDTA Contamination
In this example, the blood was poured from a lavender top tube containing K3 EDTA into a mint top tube. The potassium from the additive causes it to appear above linearity. The anticoagulant also chelates calcium, causing it to fall below linearity. It is important to recognize the signs of EDTA contamination so that these spurious results do not get reported.
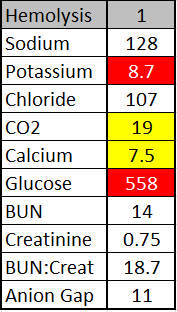
IV Contamination
This example shows a critically high potassium and glucose. These results were flagged with delta checks, meaning there were significant differences from their last blood draw. The patient did not have any history of high glucose, so that was immediately suspicious. Looking at their current medications, it was noted the patient was receiving intravenous potassium chloride and dextrose. The values are the result of contamination from these fluids.
Quick Summary
-Symptoms-
Hypokalemia
↓ K
Muscle Twitching
Irregular Heartbeat
Muscle Cramps
Hyperkalemia
⭡ K
Muscle Weakness
Arrhytmia
Numbness/Tingling
-Causes-
Hypokalemia
↓ K
Vomiting
Diarrhea
Diuretics
Cushing syndrome
–
Hyperkalemia
⭡ K
Kidney Problems
Dehydration
Severe Tissue Injury
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Excessive Supplementation
-Spurious Results-
Pseudohyperkalemia
⭡ K
Hemolysis
EDTA Contamination
IV Fluid Contamination
Thrombocytosis
Extreme Leukocytosis
References
- Potassium Blood Test: MedlinePlus Medical Test
- Potassium | Pathology Tests Explained
- ROCHE – eLabDoc
- Potassium – Medicine LibreTexts
- Laboratory Test Handbook with Disease Index 2nd Edition – Lexi-Comp’s Clinical Reference Library
- Overview of Disorders of Potassium Concentration – Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders – Merck Manual Professional Edition
- Hypokalemia – Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders – Merck Manual Professional Edition
- Hyperkalemia – Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders – Merck Manual Professional Edition
- Pseudohyperkalemia
Authored by Rachel Harper, Medical Laboratory Scientist (ASCP)
Last reviewed: February 2026
For educational and reference purposes only, this is not medical advice.