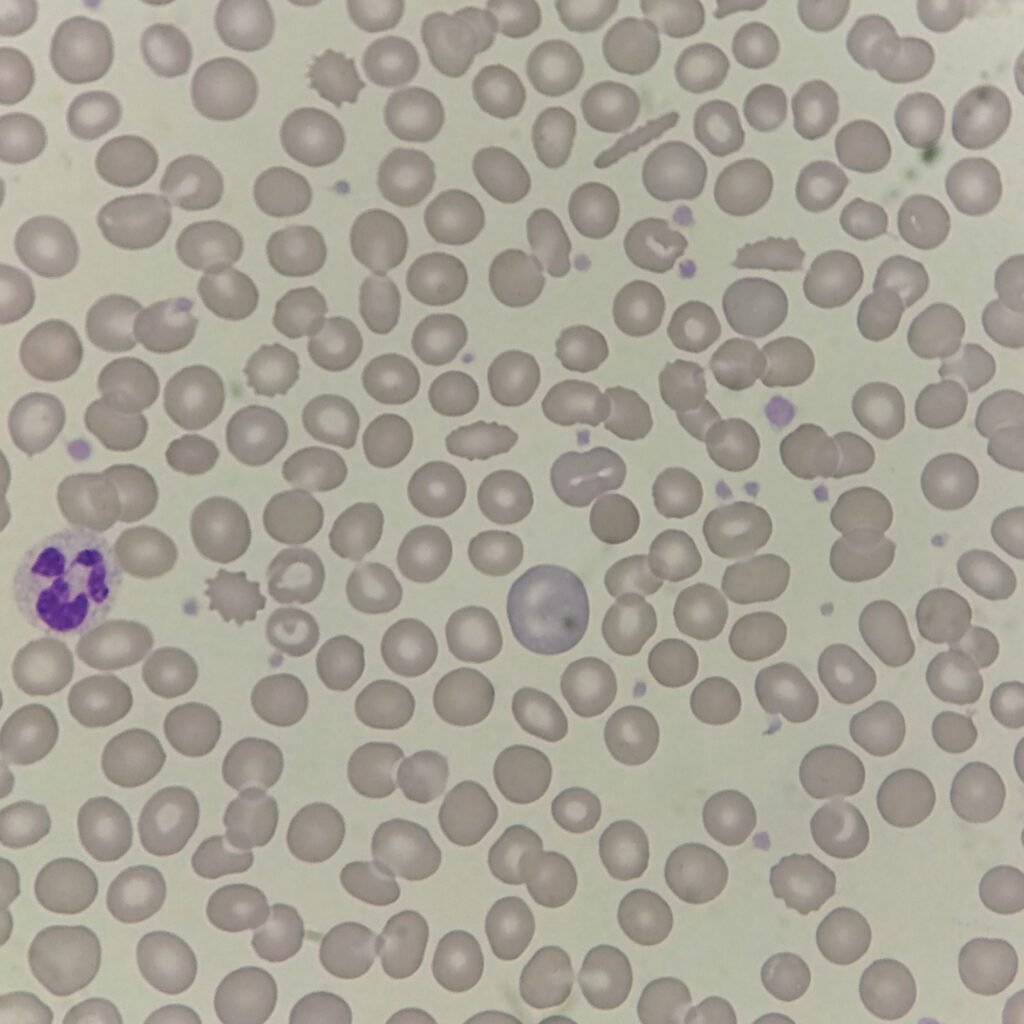
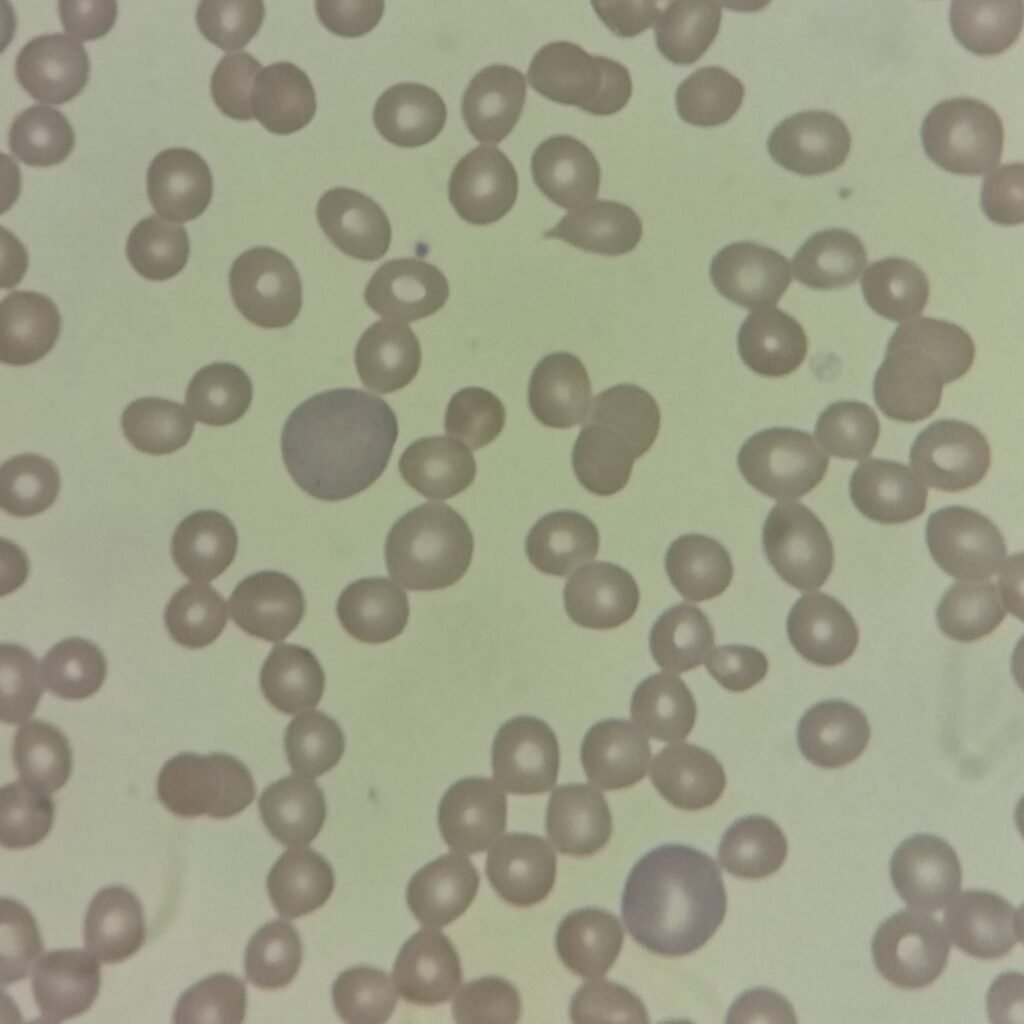
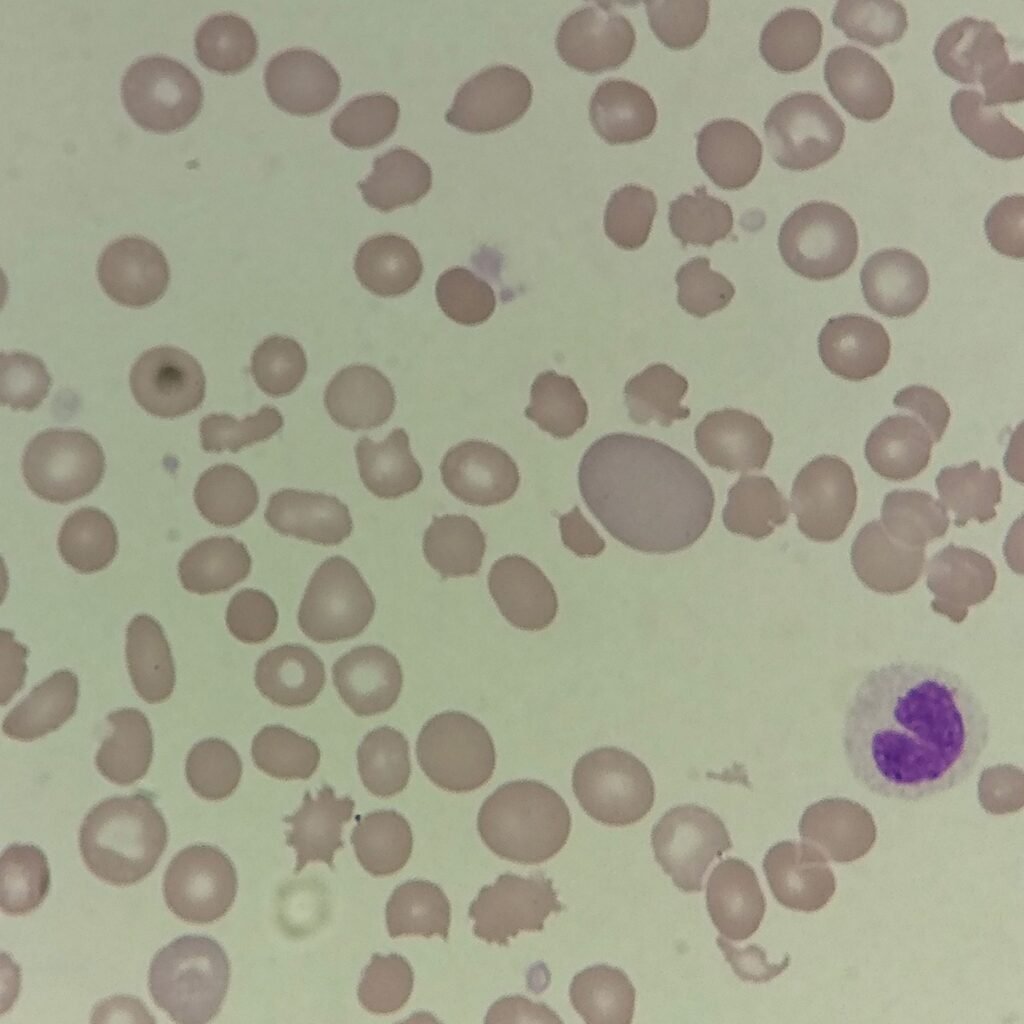
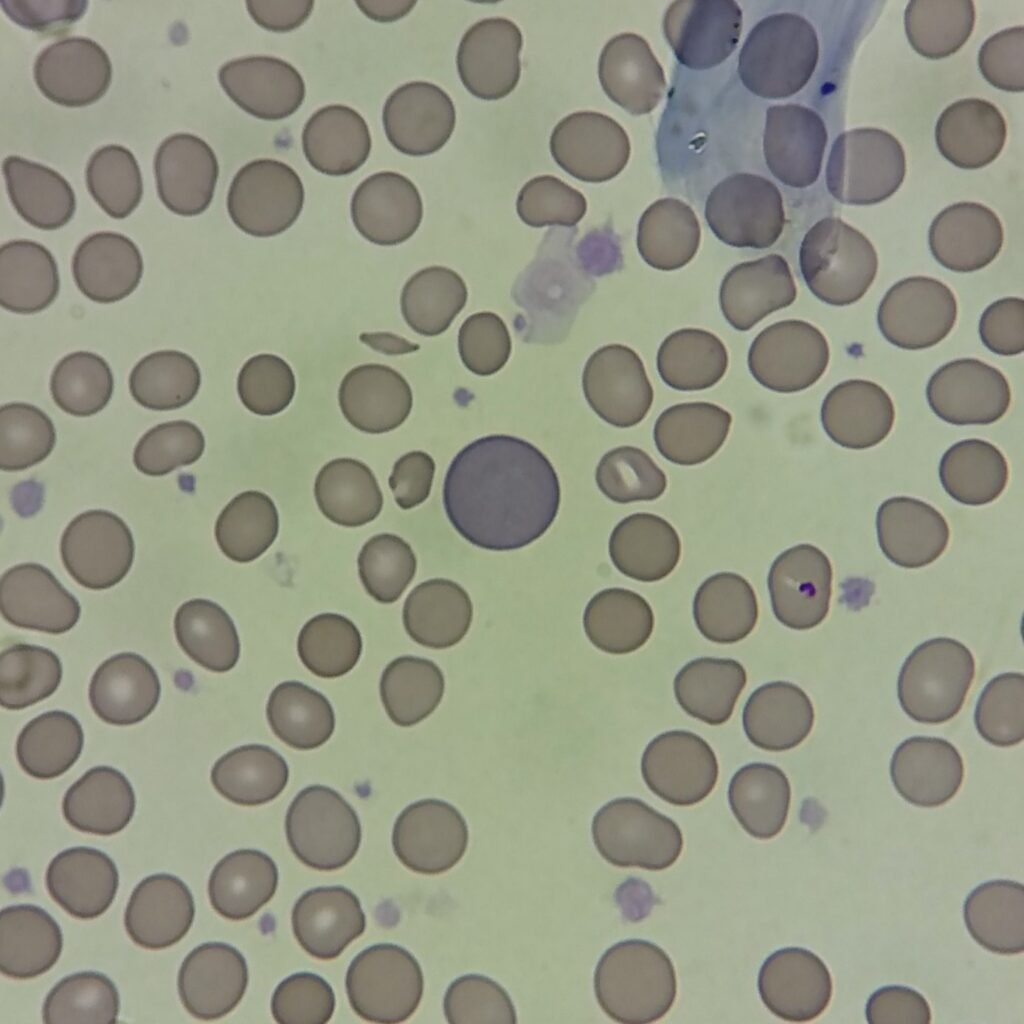
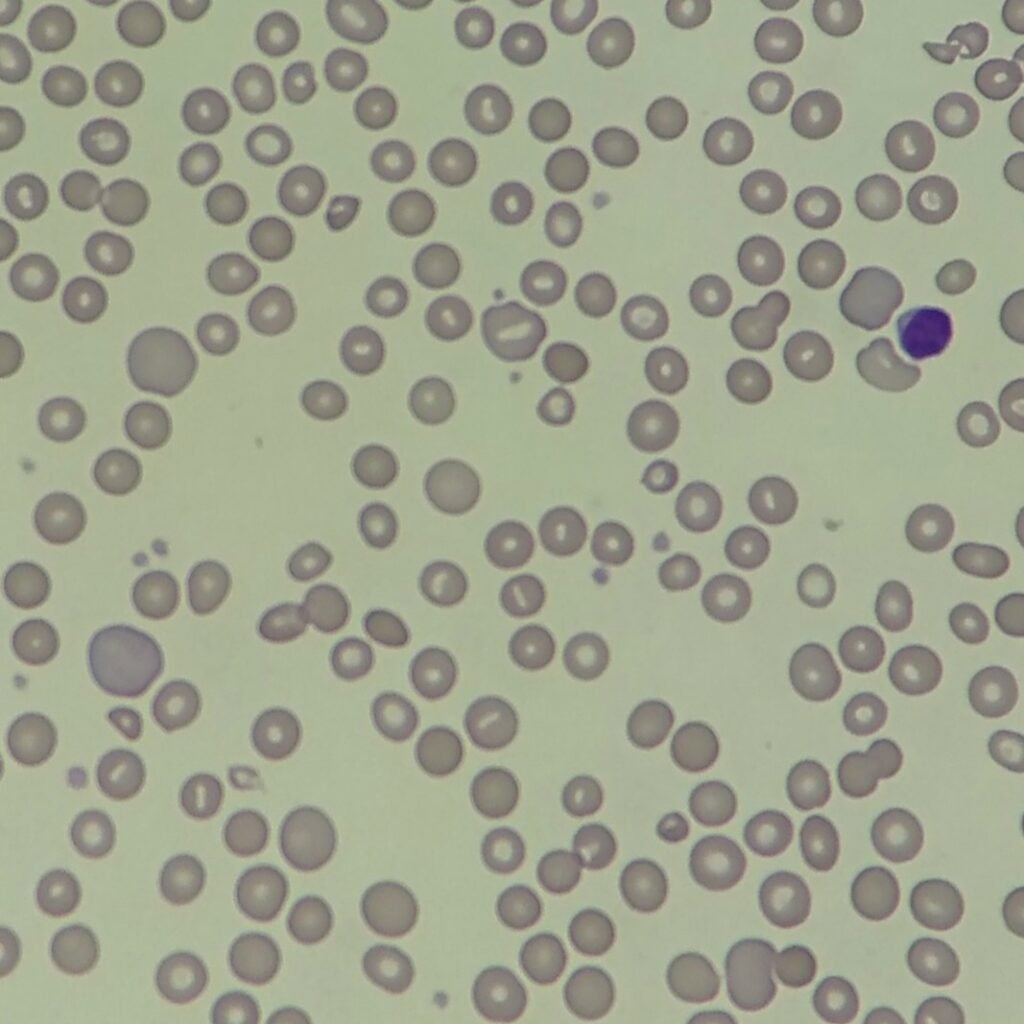
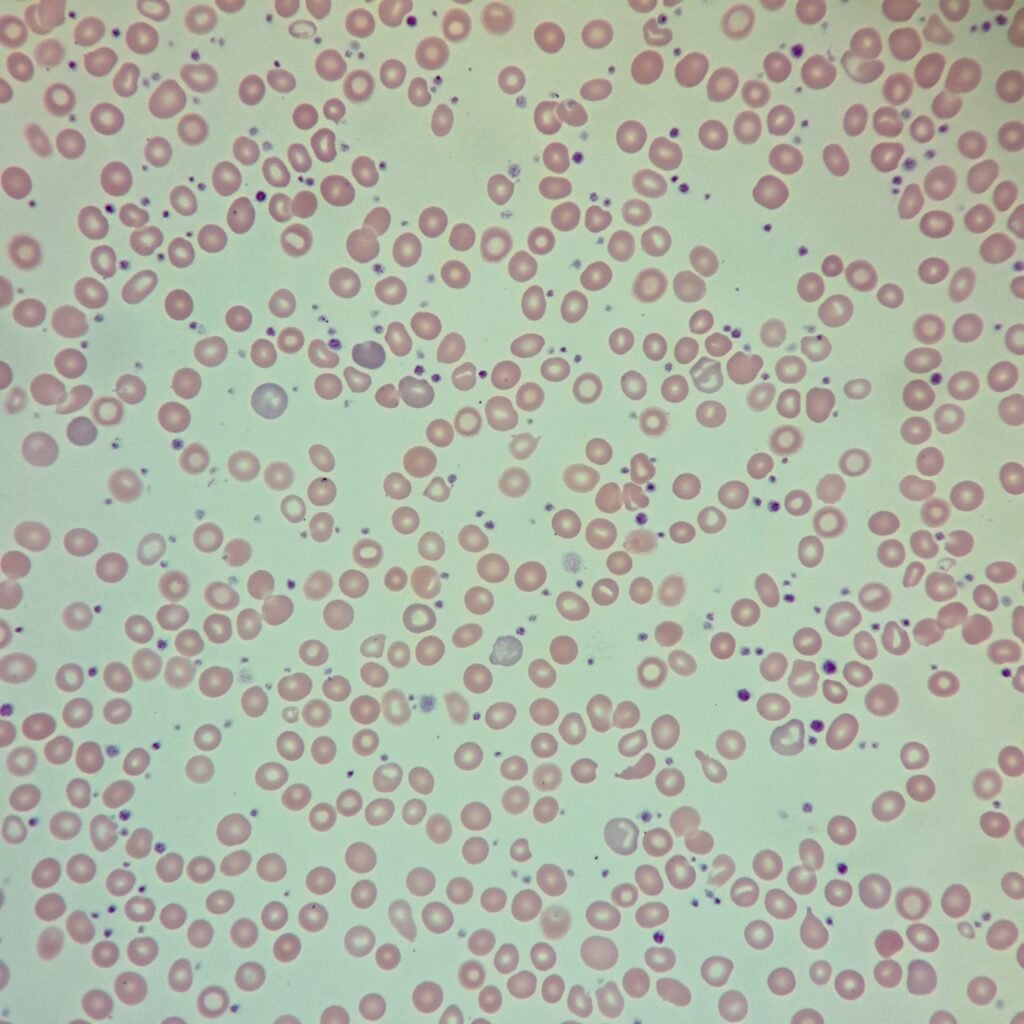
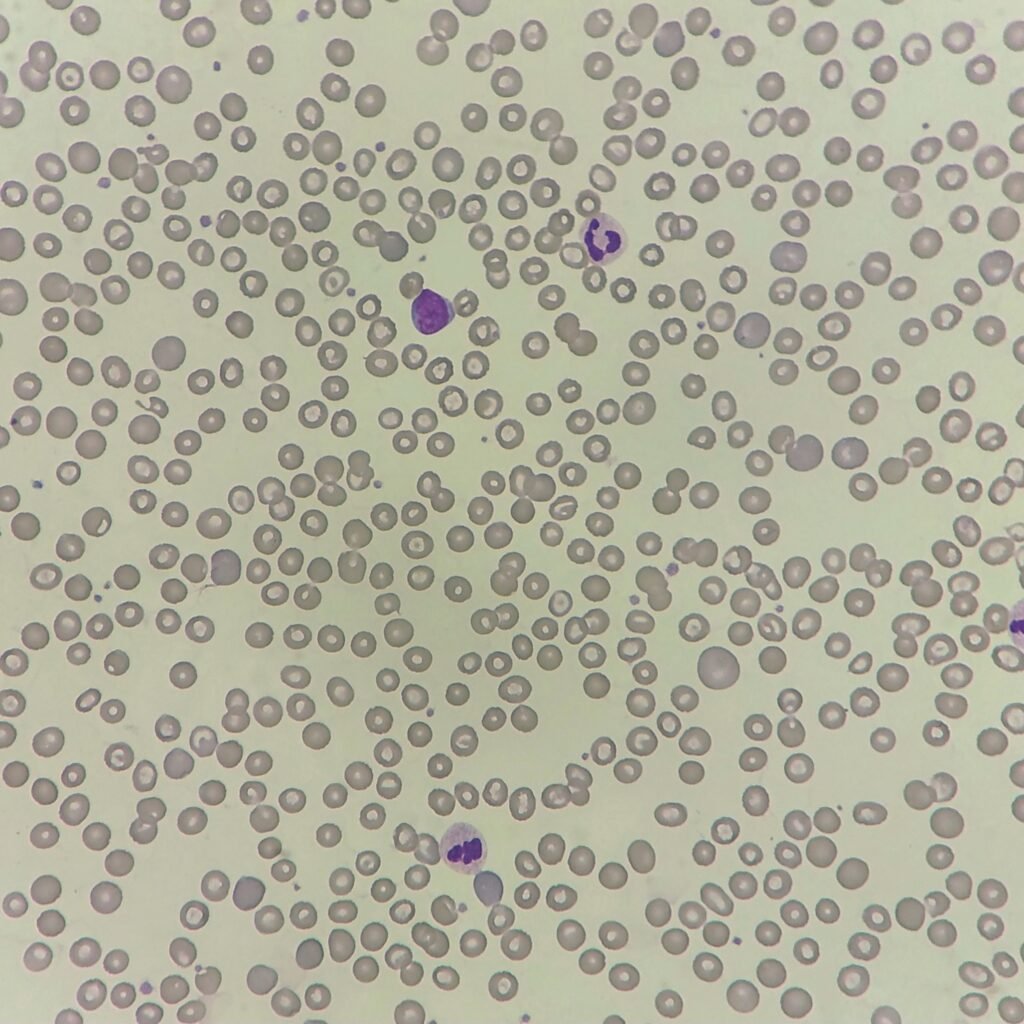
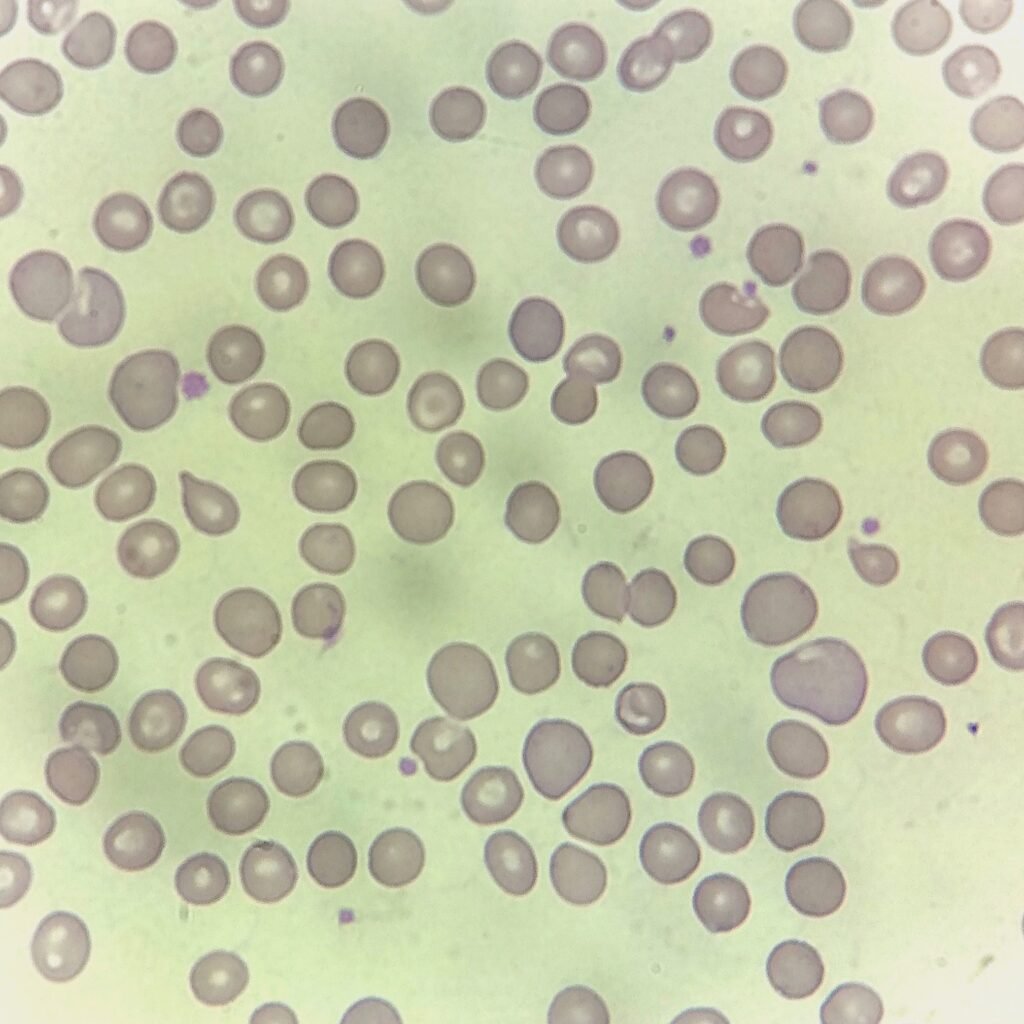
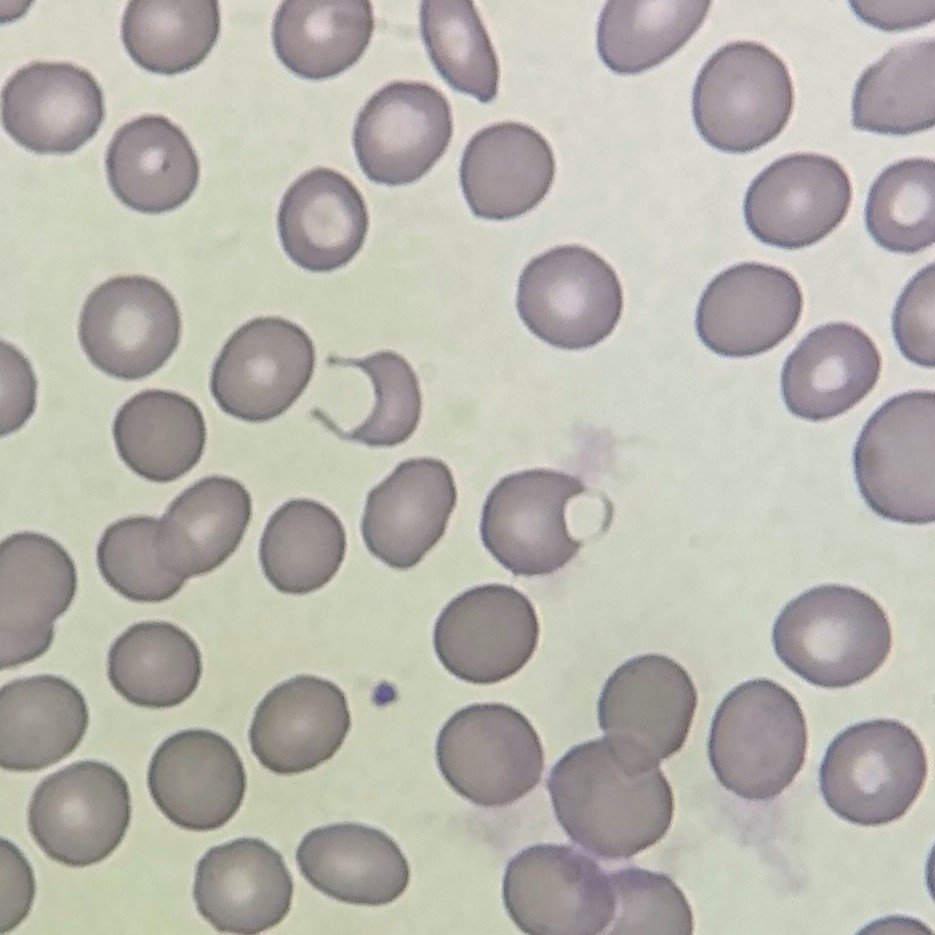
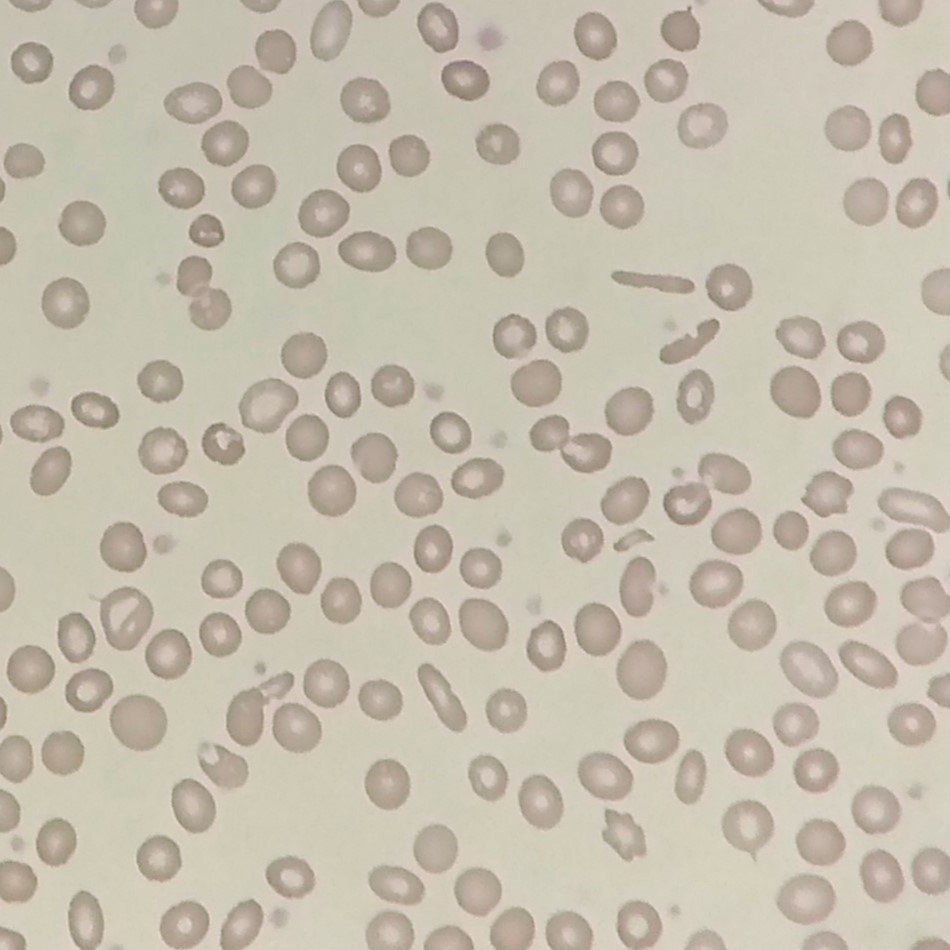
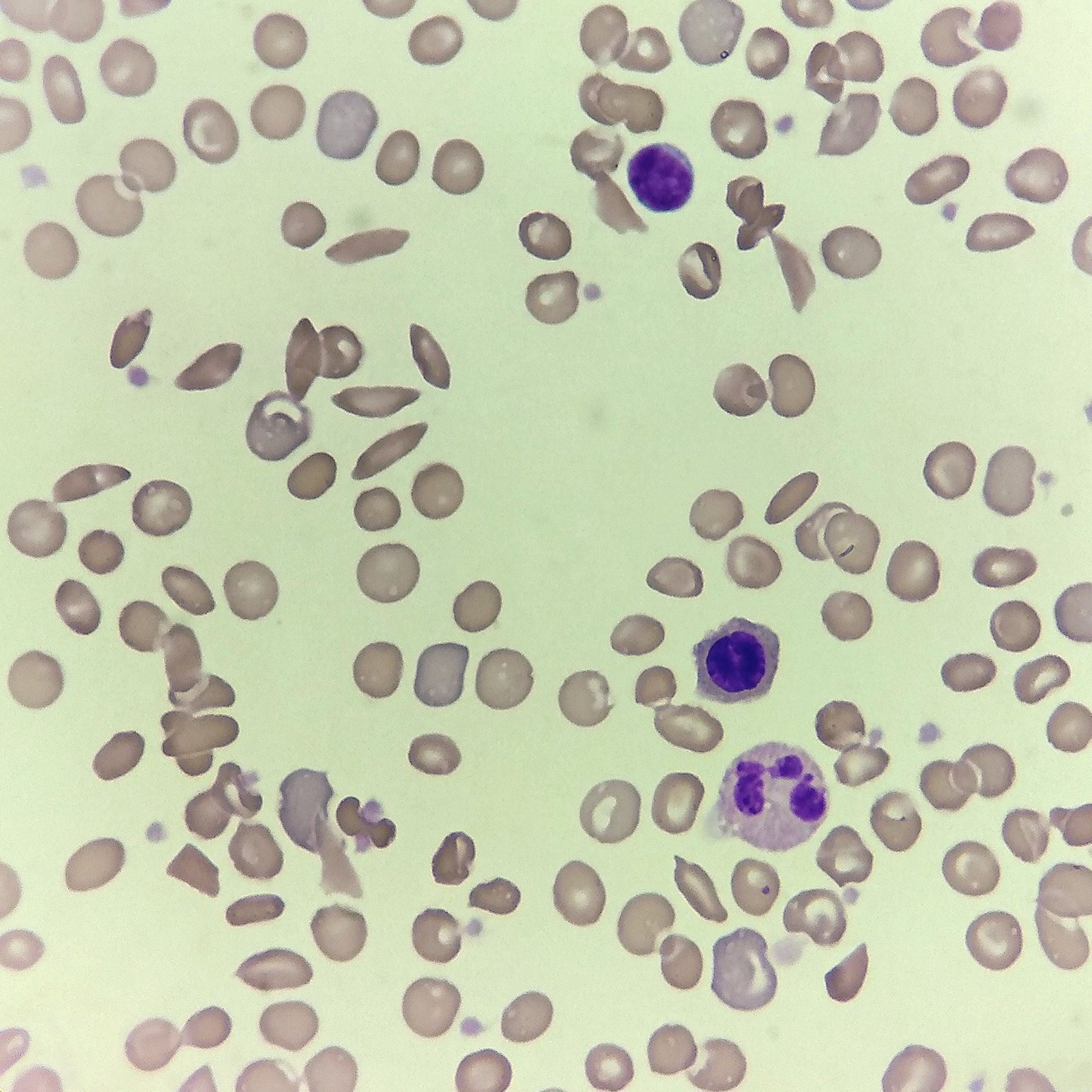
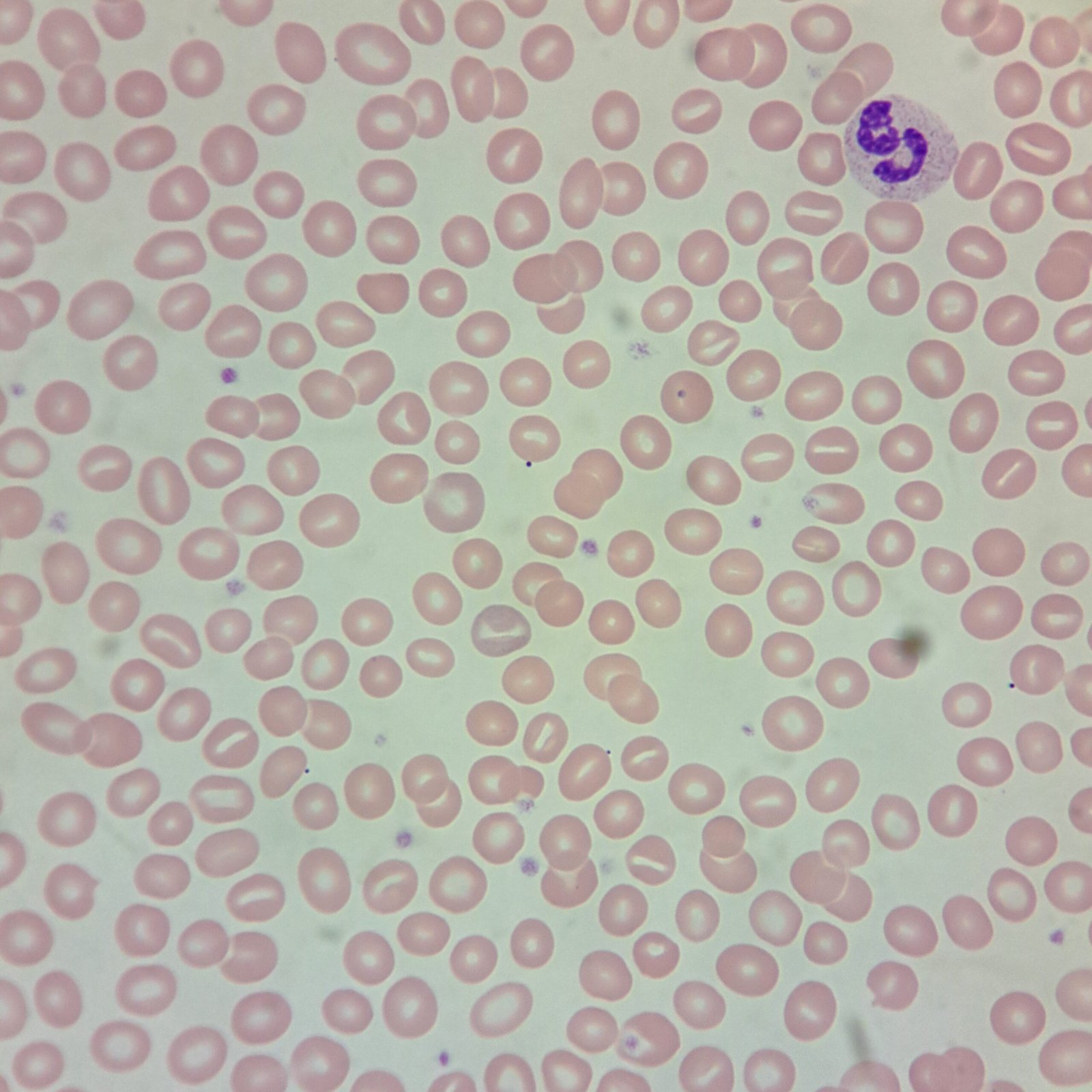
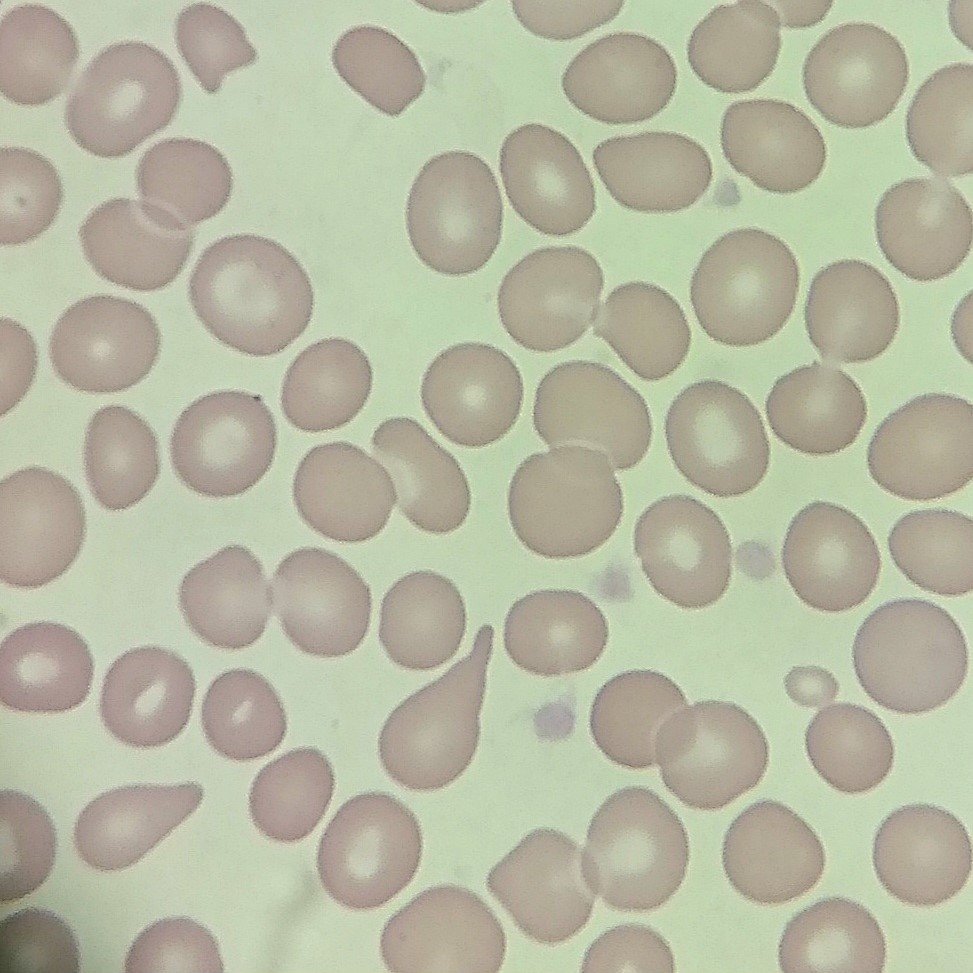
Polychromasia refers to the presence of polychromatophilic red blood cells that stain with a blue hue due to residual RNA. As polychromatic cells are immature, they should be proportional to the reticulocyte percentage. However, a supravital stain would be required to positively identify these cells as reticulocytes.
Polychromasia is seen in conditions with increased erythropoiesis such as hemolytic anemias or hemorrhages.
Appearance
Polychromatic red blood cells stain diffusely purple or blue/gray due to residual RNA. They may be slightly larger than mature red blood cells.
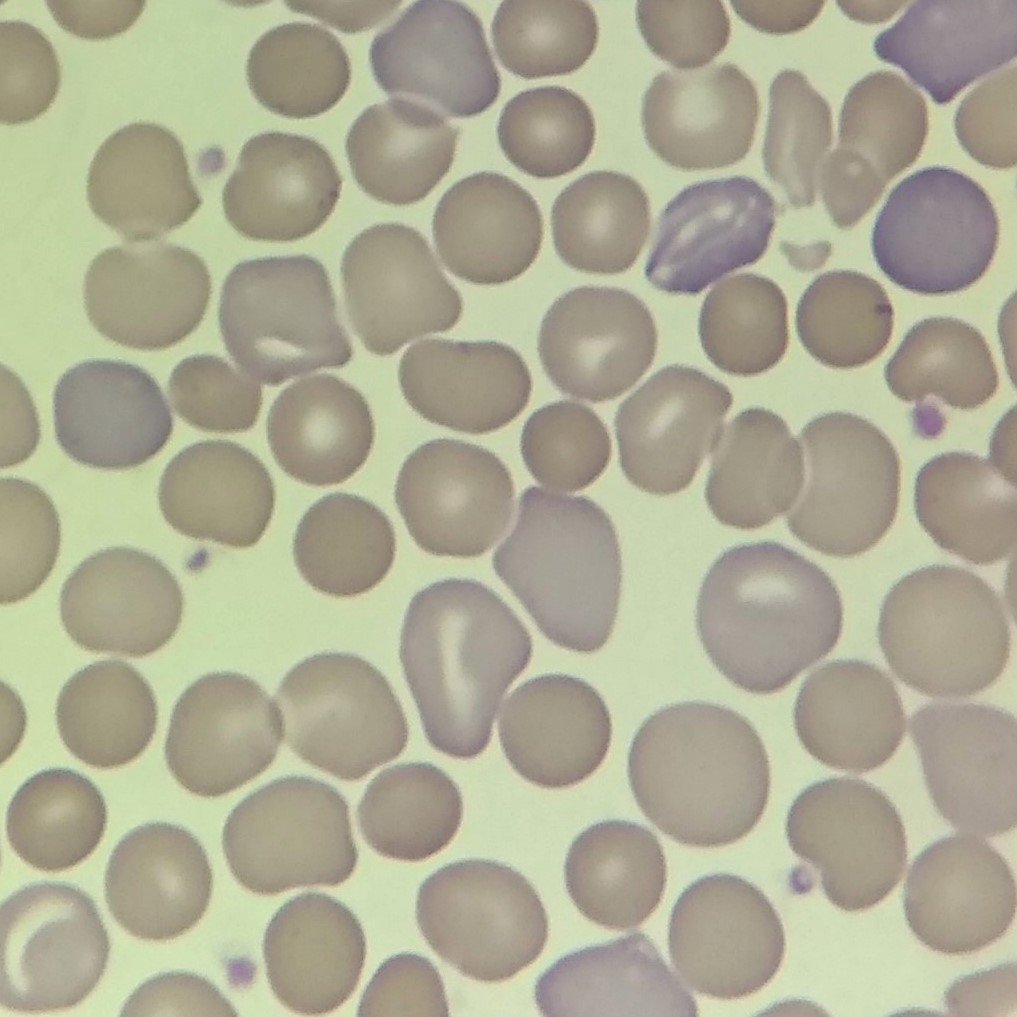
Lookalikes
Polychromatic cells can have very fine basophilic stippling which is evenly dispersed throughout the cell. This should not be confused with coarse basophilic stippling which has larger inclusions.
Basophilic Stippling

Gallery