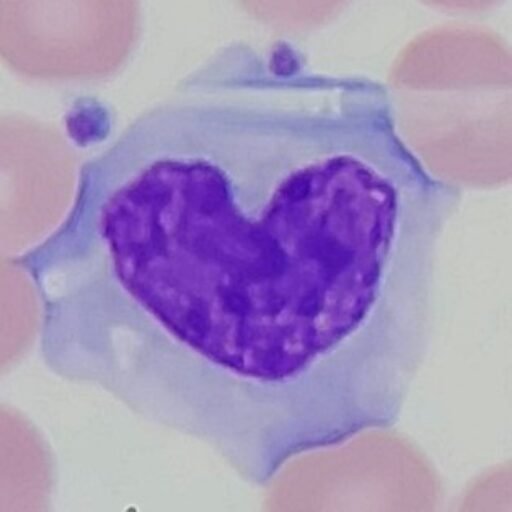
Babesia
Rings or tetrads in the cytoplasm of a red blood cell
Tick-borne parasite that causes babesiosis. Usually only affects susceptible populations.
Basophilic Stippling
Coarse stippling is more readily apparent with evenly dispersed larger granules.
Seen in Lead Poisoning, Thalassemia, Sideroblastic Anemia, Megaloblastic Anemias, Defective Heme Synthesis.
Fine stippling appears as evenly distributed purple dust and is hard to see in a cell. Often times fine stippling is seen in reticulocytes from residual RNA. Typically not clinically significant. See polychromatic cells.

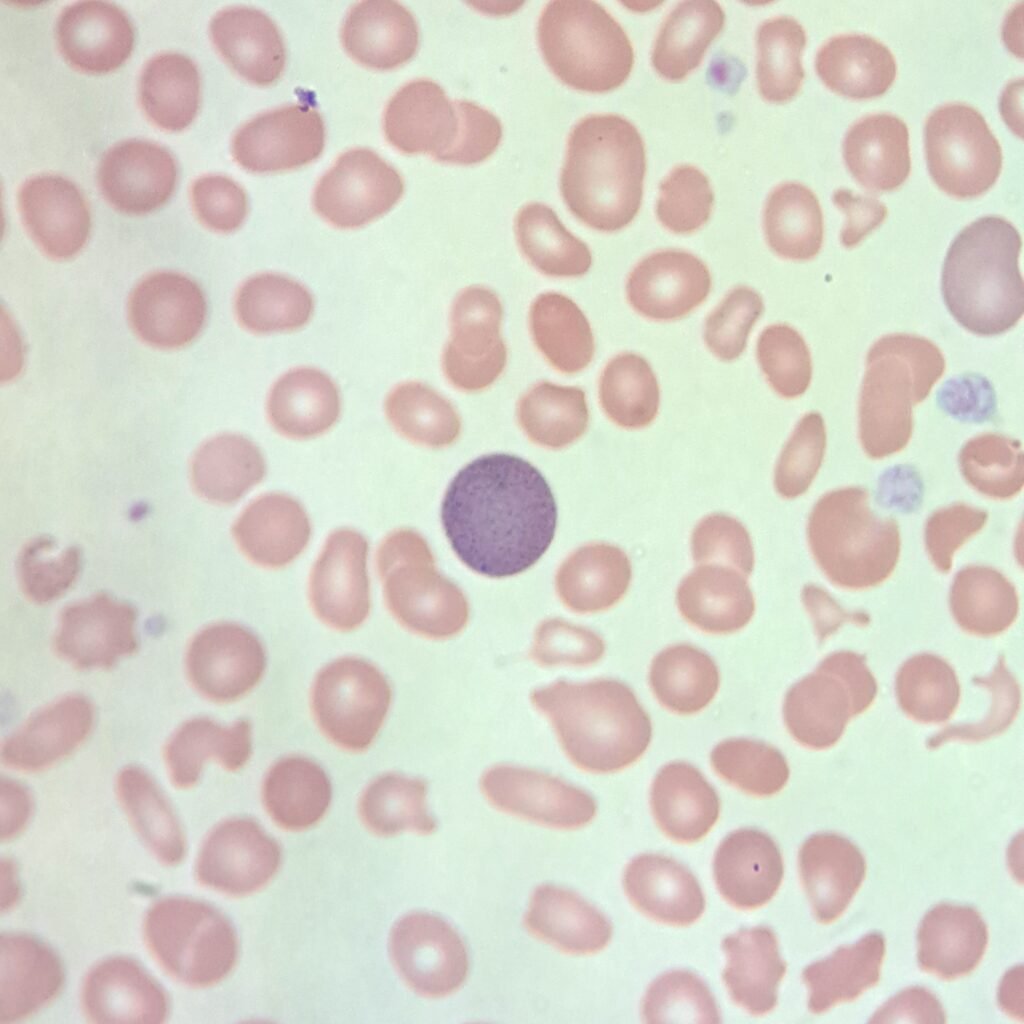
Cabot Ring
Oval or figure-8 inclusion consisting of nuclear remnants or part of the mitotic spindle
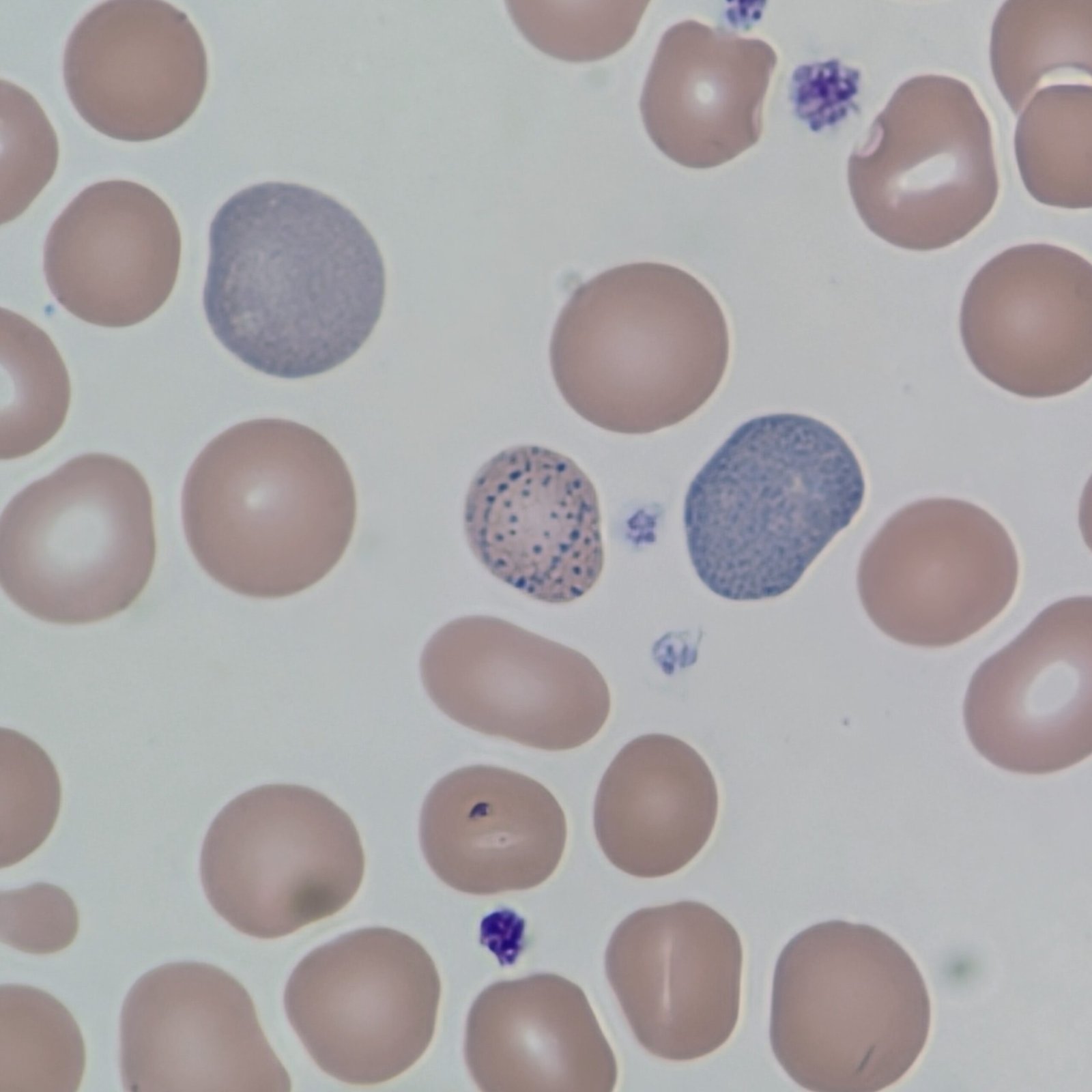
Hemoglobin C Crystals
Densely red staining crystal with the hemoglobin concentrated to a rhomboid rod-shaped area
Caused by being homozygous for the abnormal Hemoglobin C gene. Seen more often in those of African descent.
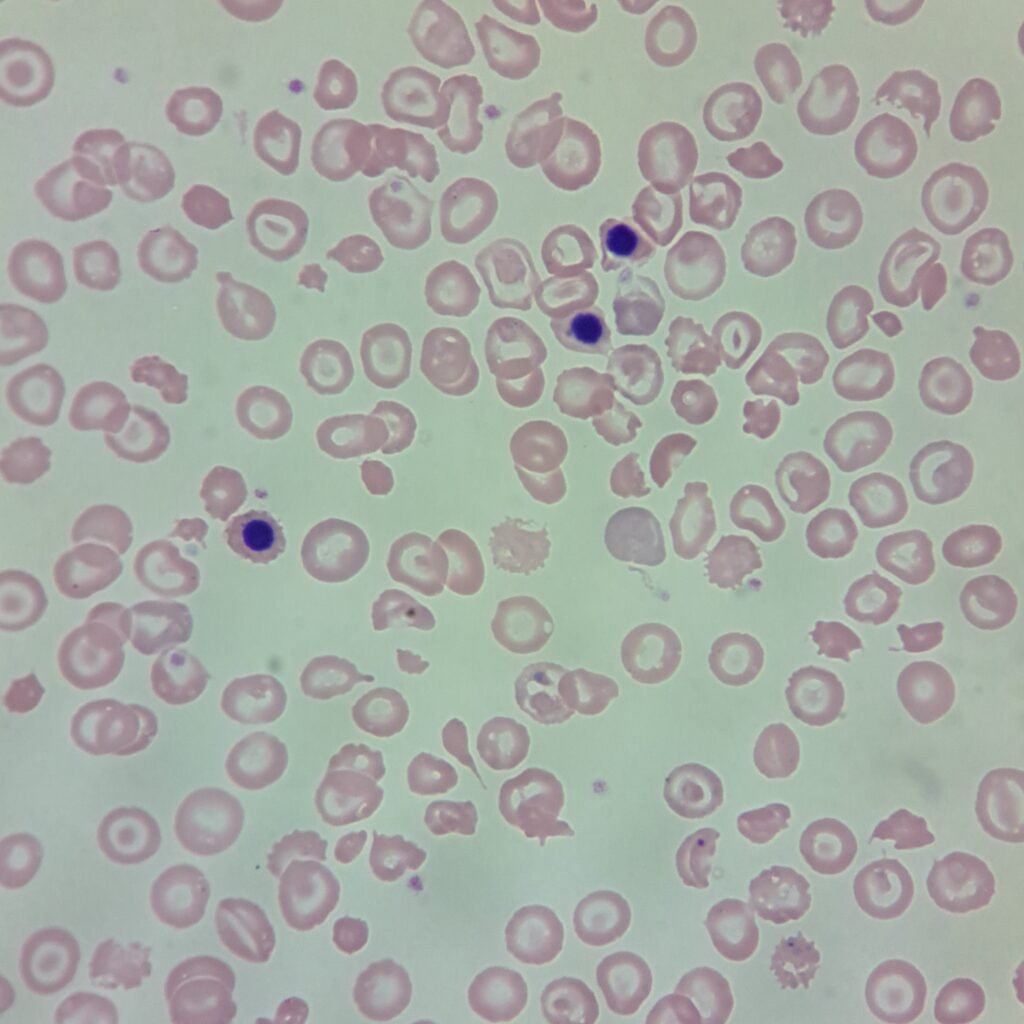
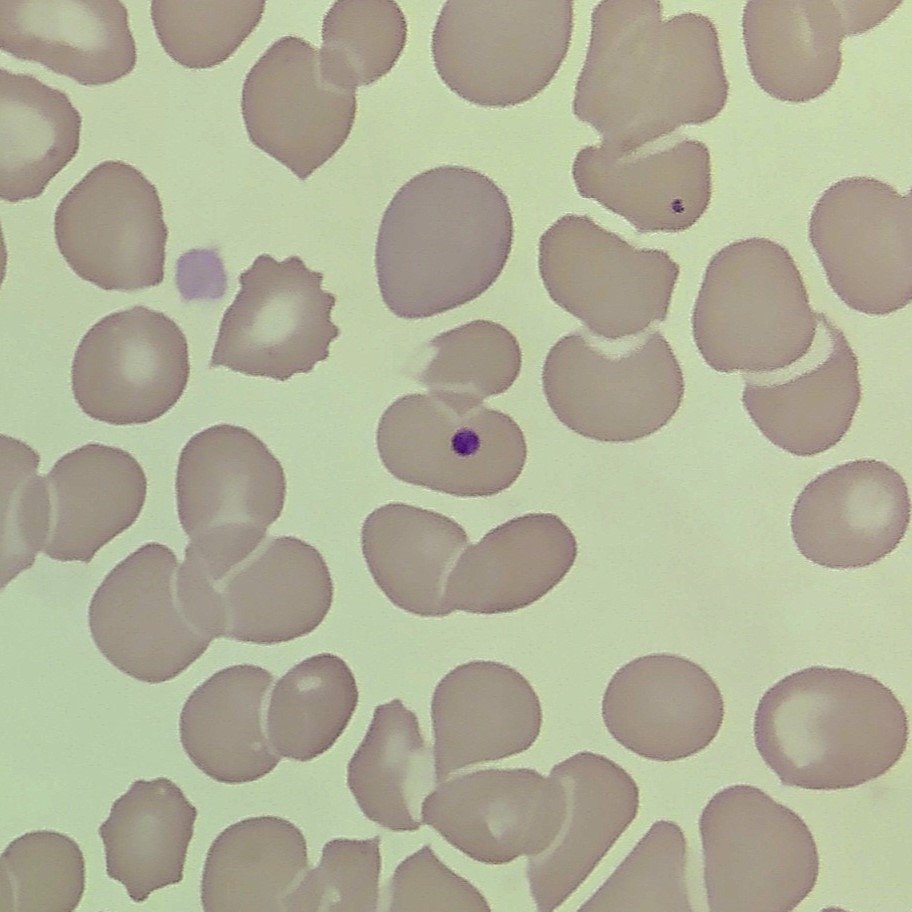
Howell-Jolly Bodies
Densely staining purple nuclear fragment, usually appearing single granule.
Seen in Megaloblastic Anemias, Hemolytic Anemias, Hyposplenism, Post-splenectomy, Alcoholism, Sickle Cell Anemia.
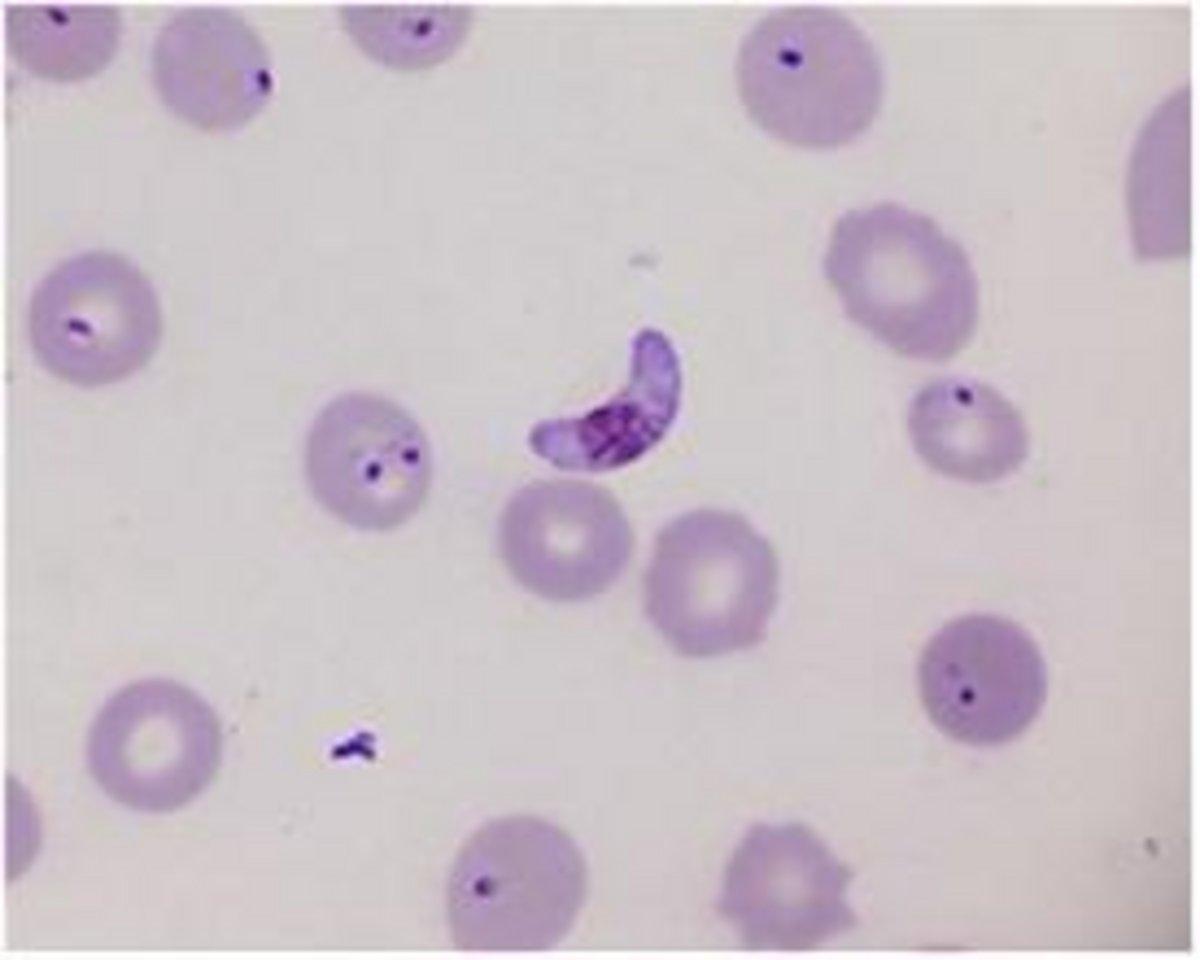
Malaria
There are five different species of plasmodium that can cause malaria in humans: P. falciparum, P. malariae, P. ovale, P. vivax, and P. knowlesi. Most cases of malaria in the United States are caused by recent travel to endemic locations.
Appearance will depend on the specific species.
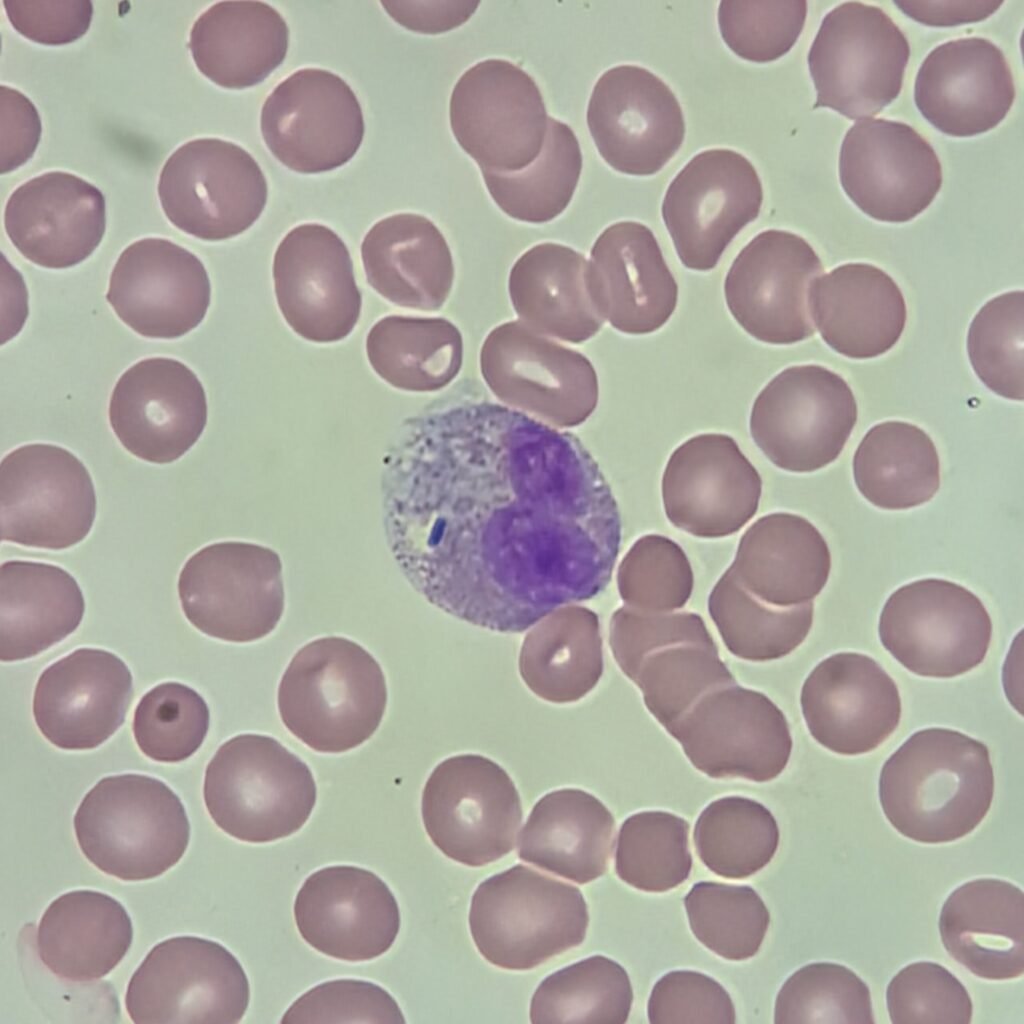
Pappenheimer Bodies
Small dark purple granules found in clusters, usually on the periphery of the cell.
Stain positive as siderotic granules with Prussian blue stain.
Seen in Sideroblastic Anemia, Hemolytic Anemia, Sickle Cell Anemia Thalassemia, Myelodysplastic Syndrome