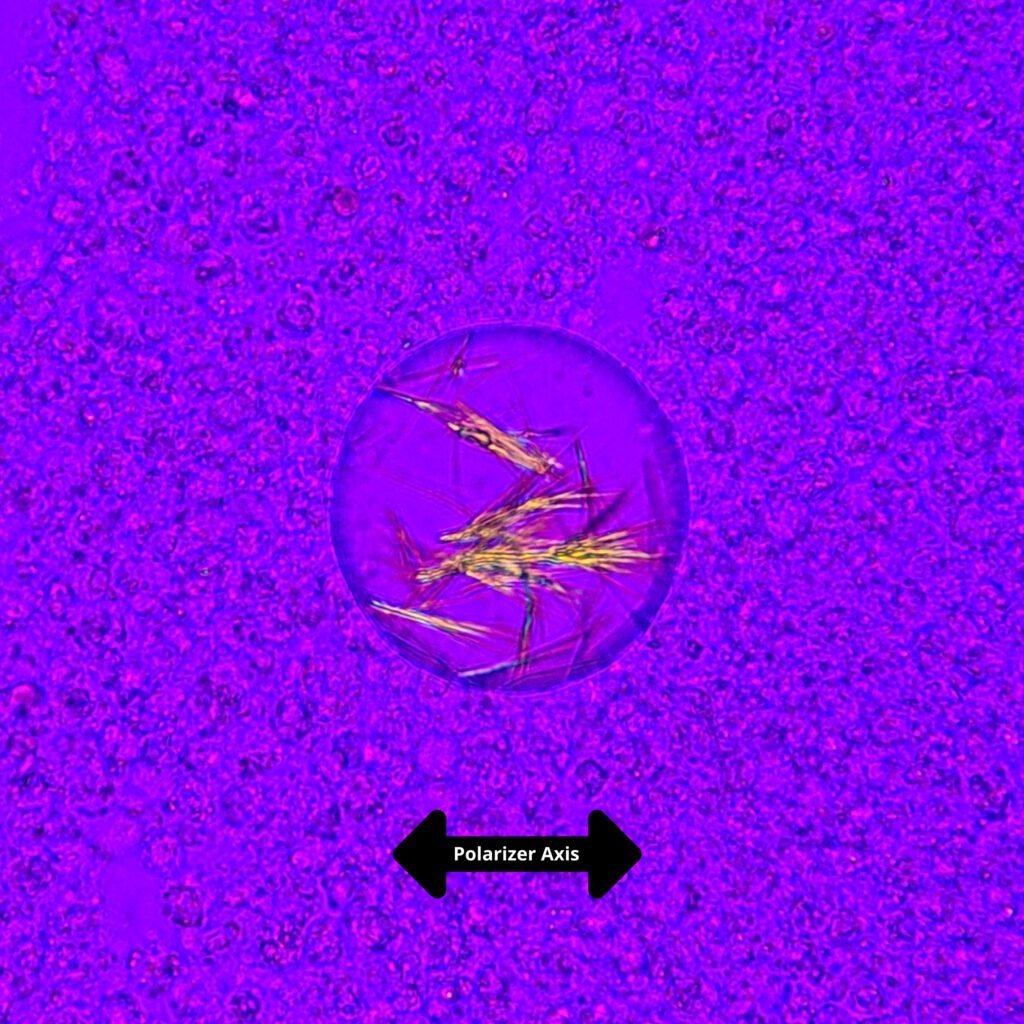
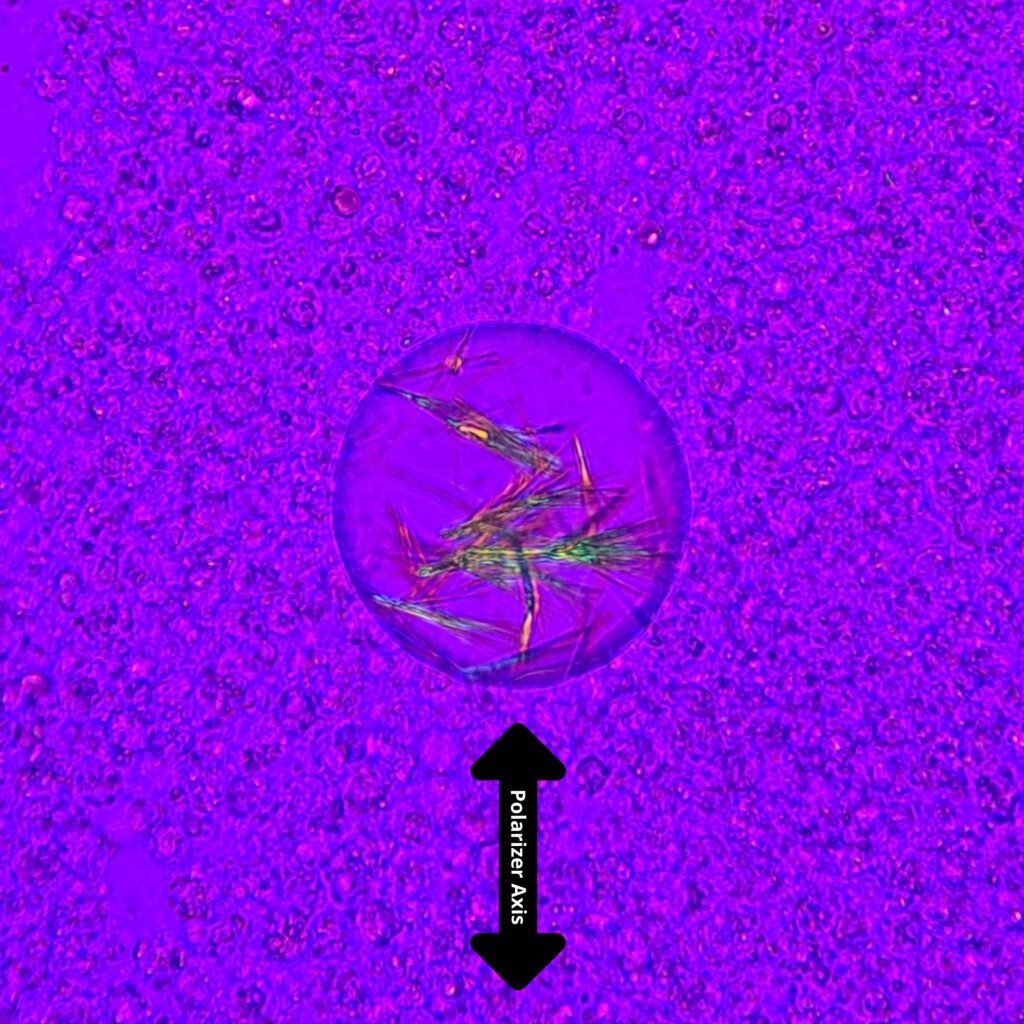
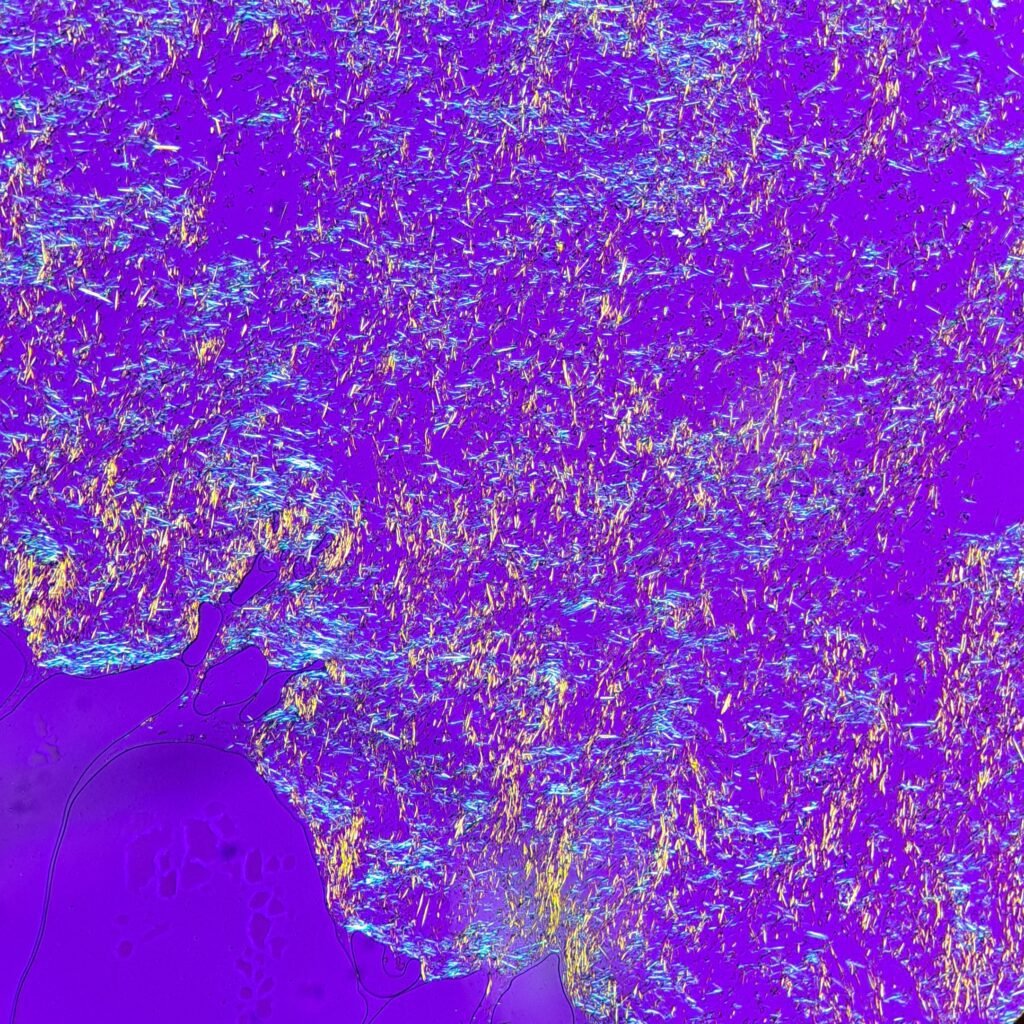
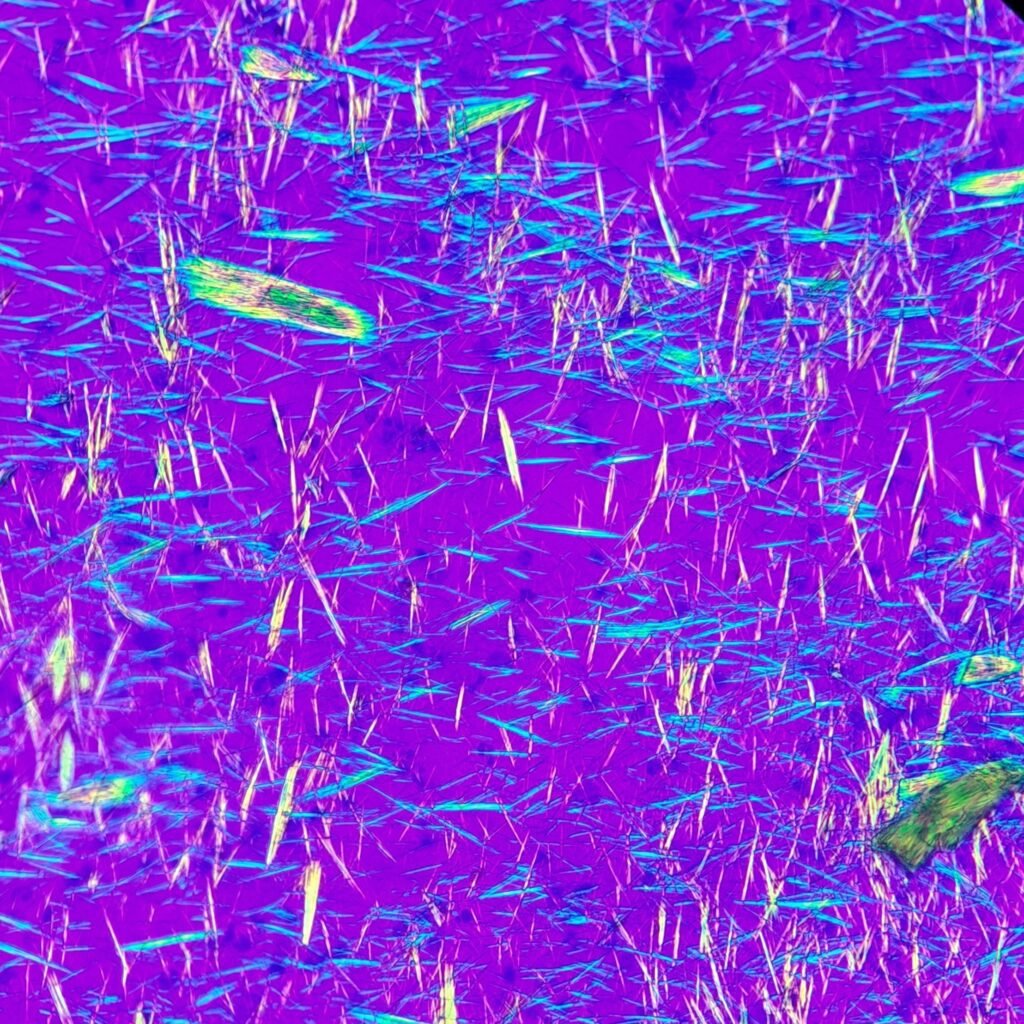
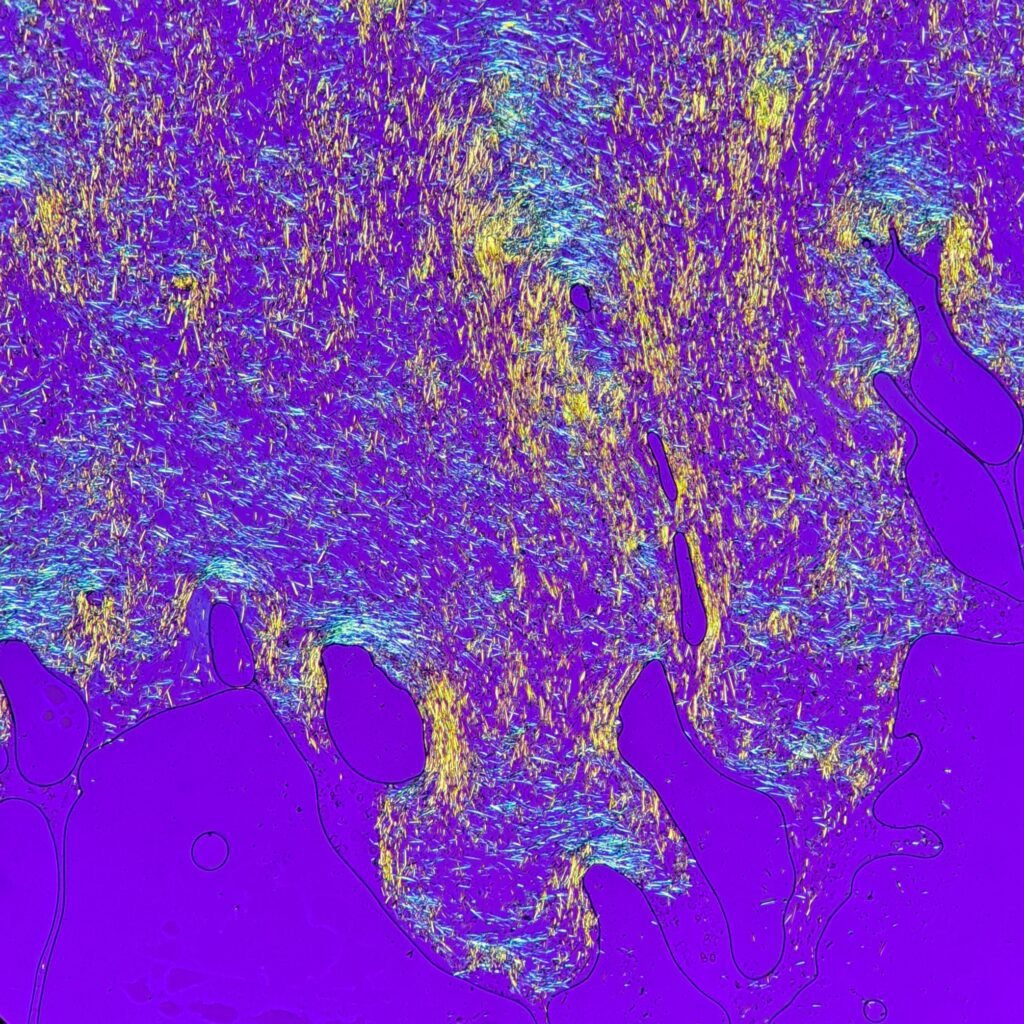
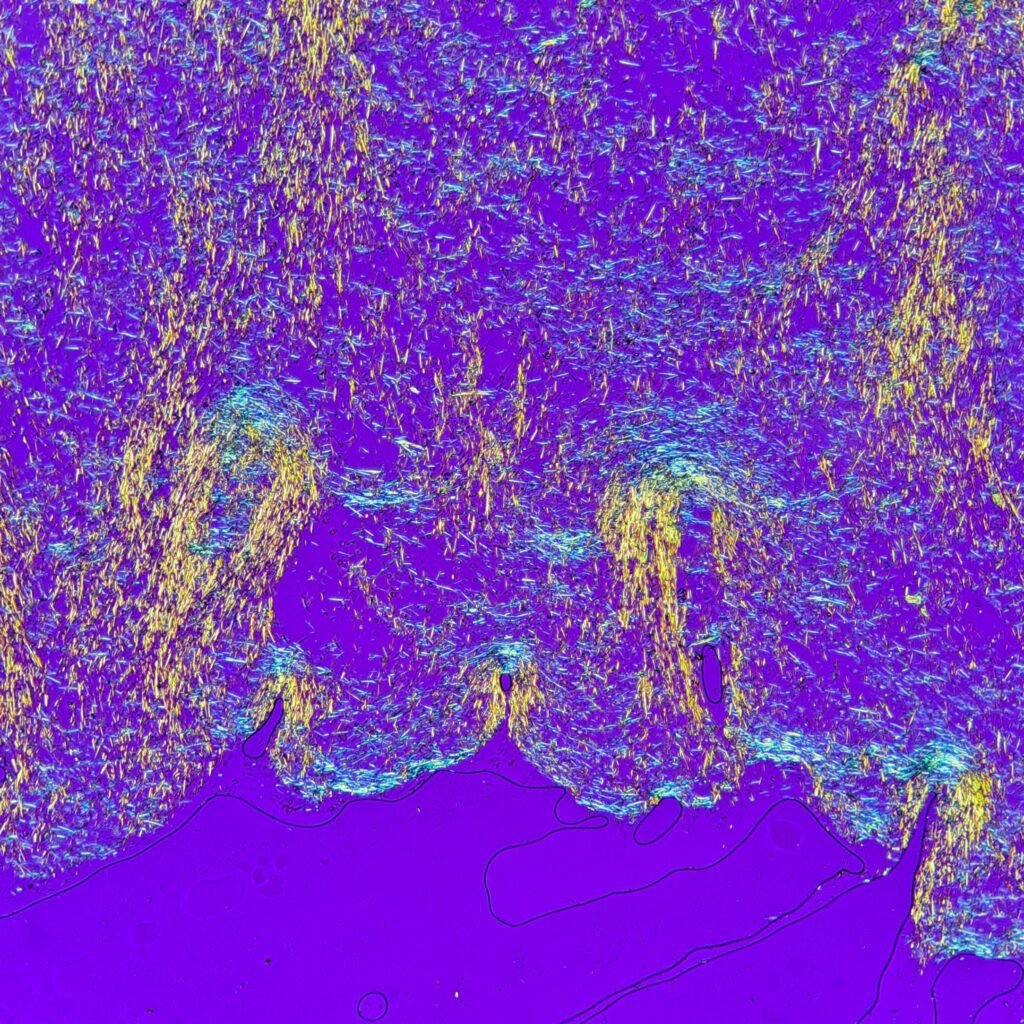
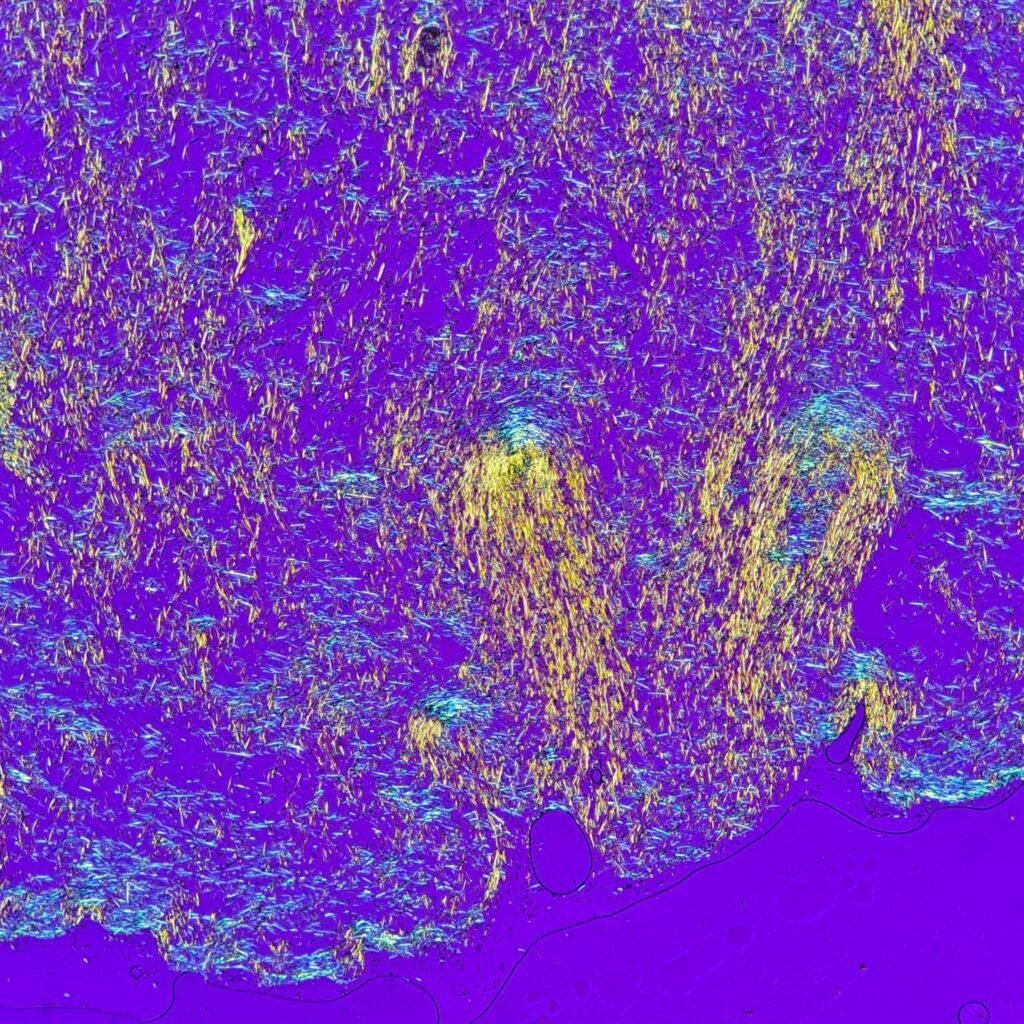
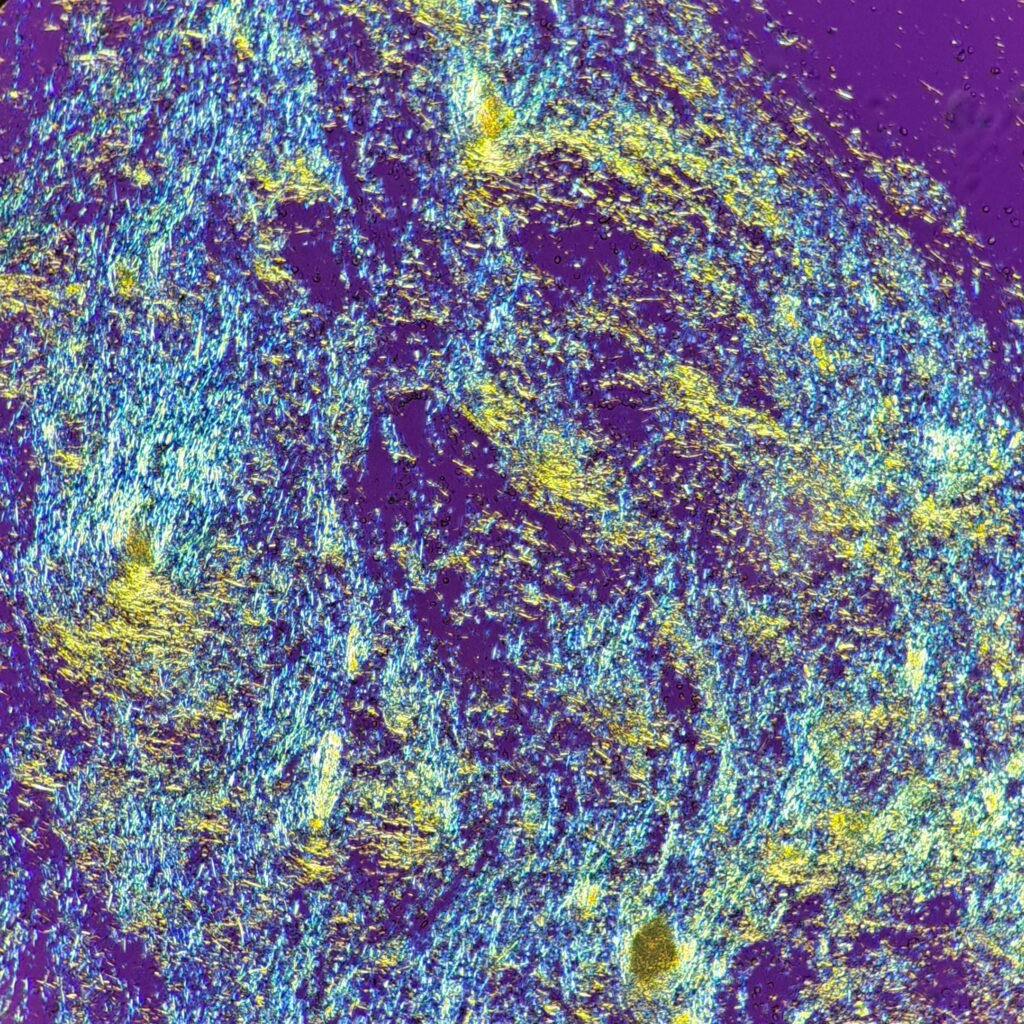
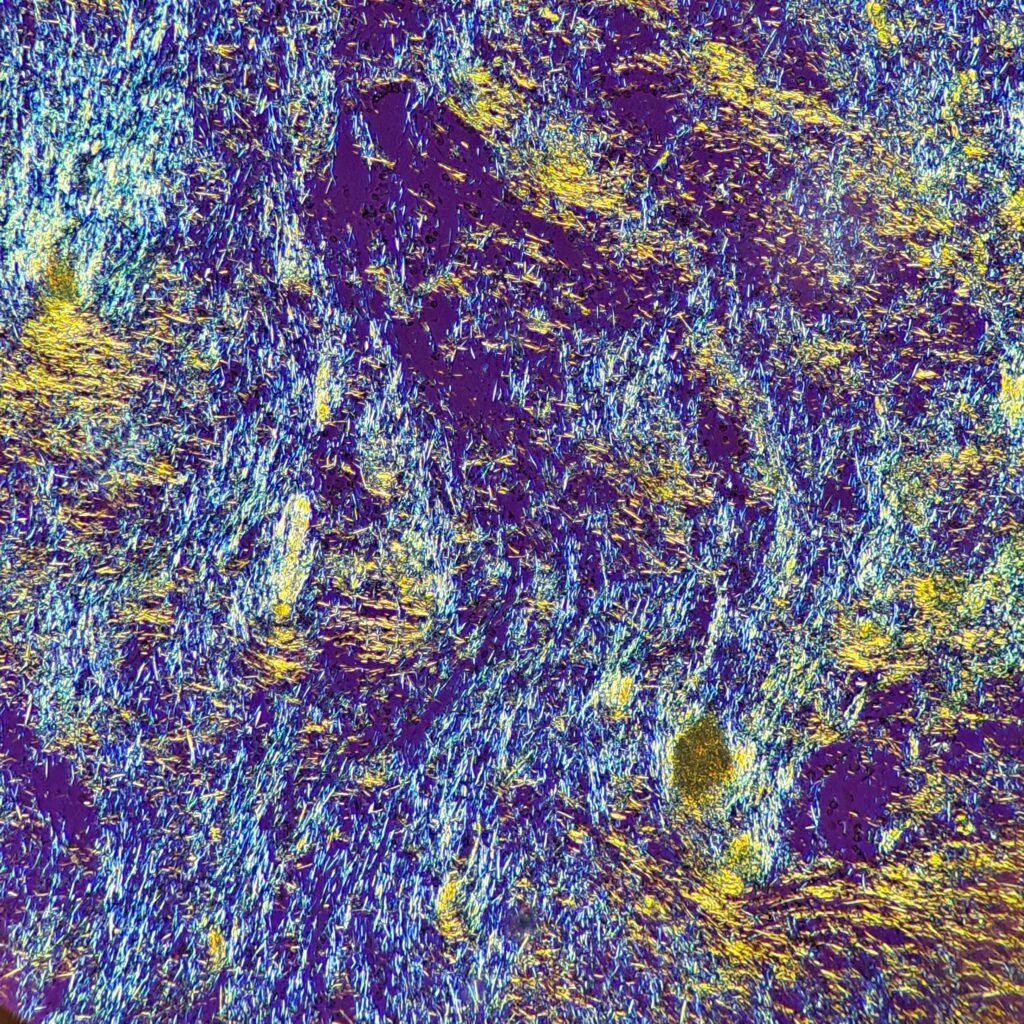
Extracellular needle-like crystals are noted in a synovial fluid. Polarization is crucial to differentiate gout from pseudogout. Monosodium urate (gout) crystals are yellow when parallel to the axis and blue when perpendicular to the axis. This is known as negative birefringence. In contrast, calcium pyrophosphate (pseudogout) crystals have positive birefringence, meaning they are blue when parallel to the axis.
See in the image comparison how the color of the crystals changes from yellow to blue based on the axis of polarization. The majority of the crystals pictured here are horizontal. When the axis is also horizontal, the parallel crystals are yellow. When the axis is vertical, the crystals are now perpendicular to the axis and appear blue. This matches with the negative birefringence of true gout crystals.
Polarizer Axis
Leave a Reply