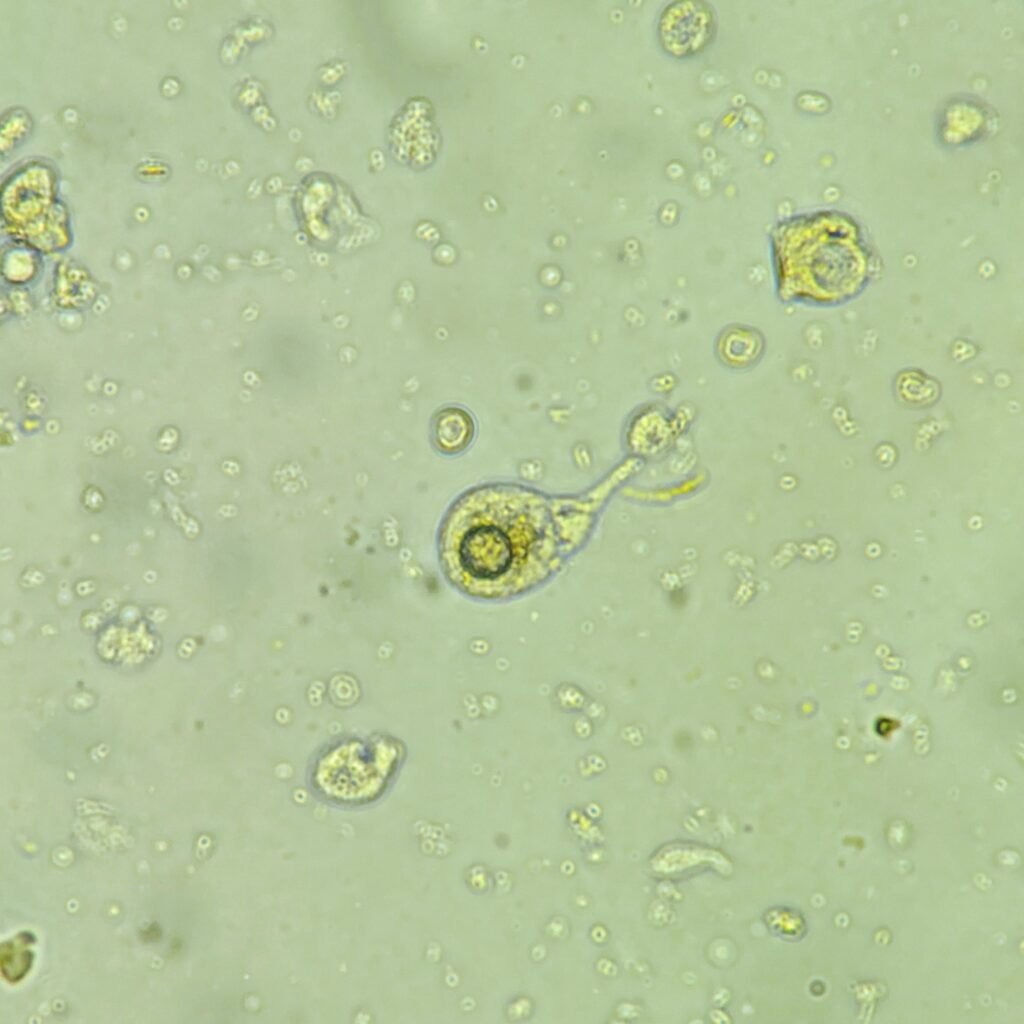
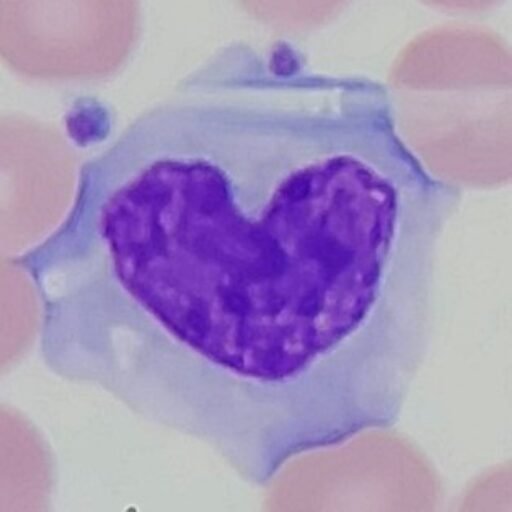
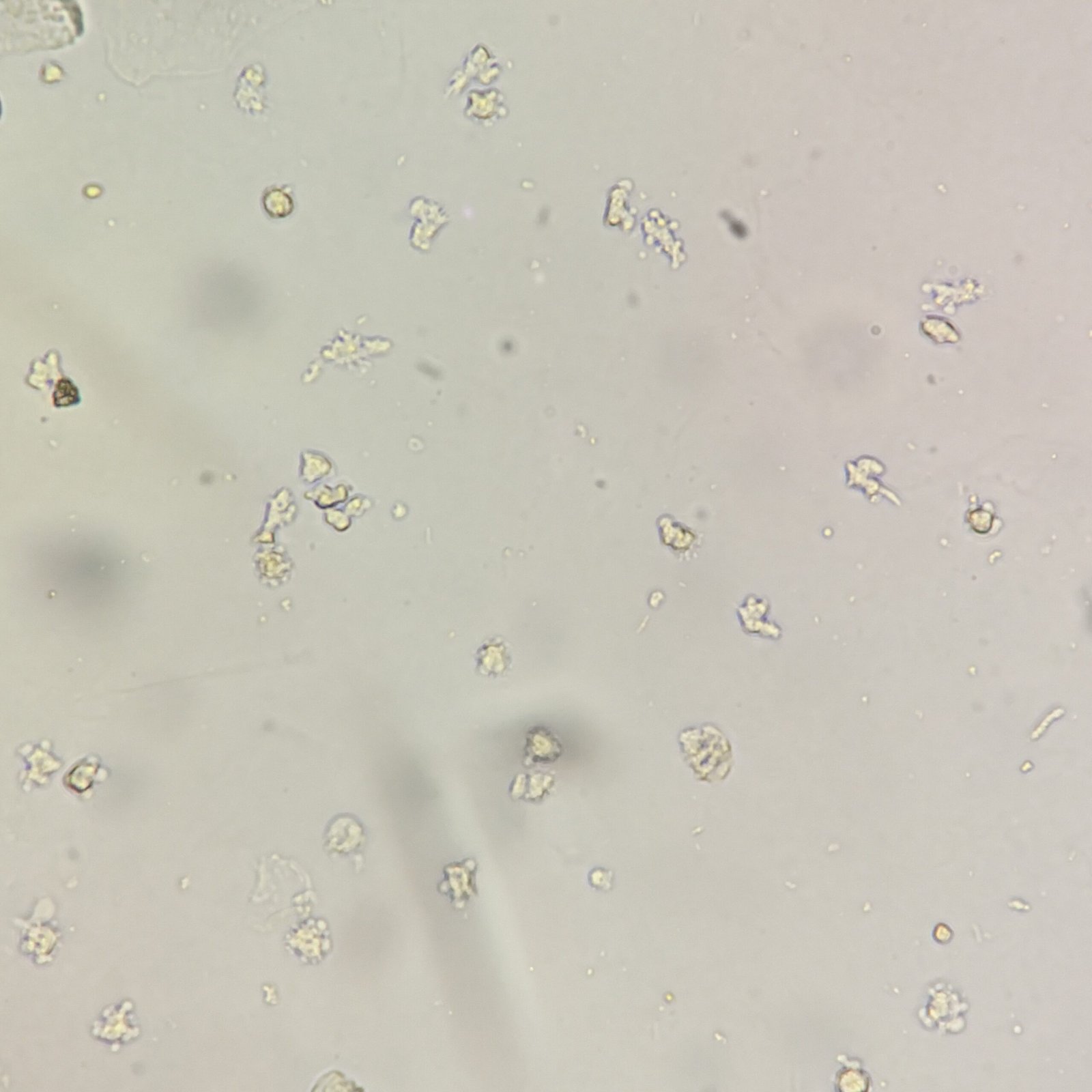
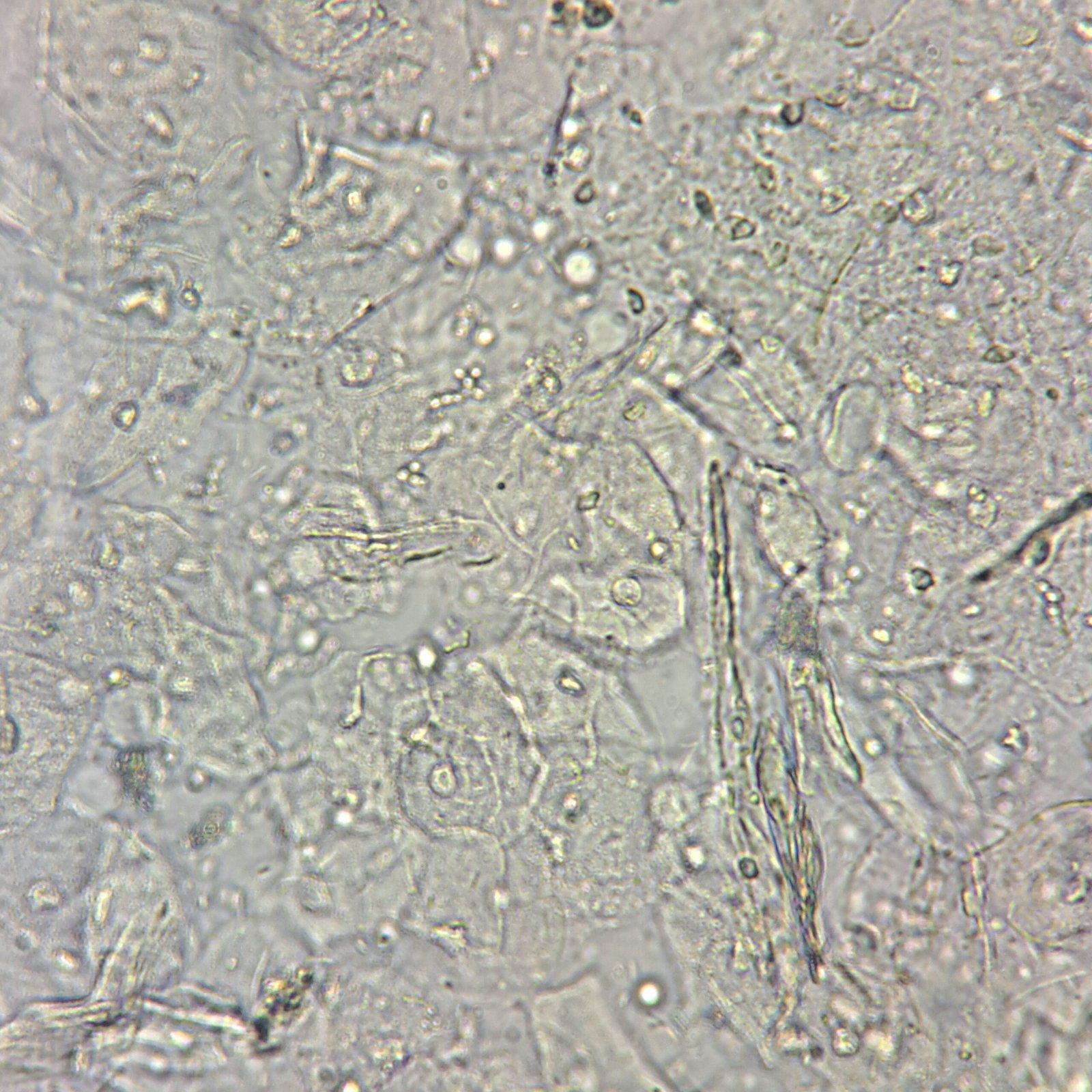
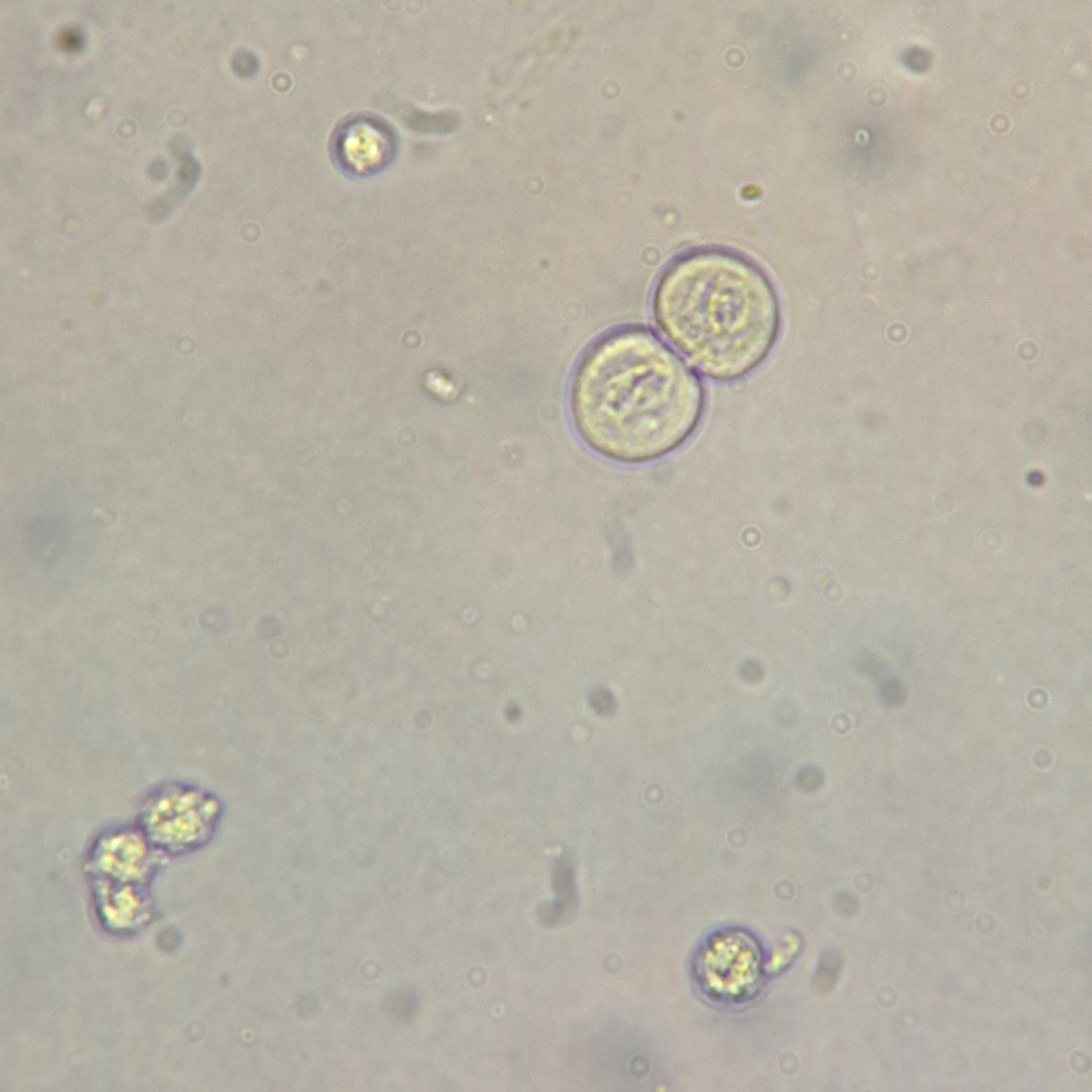
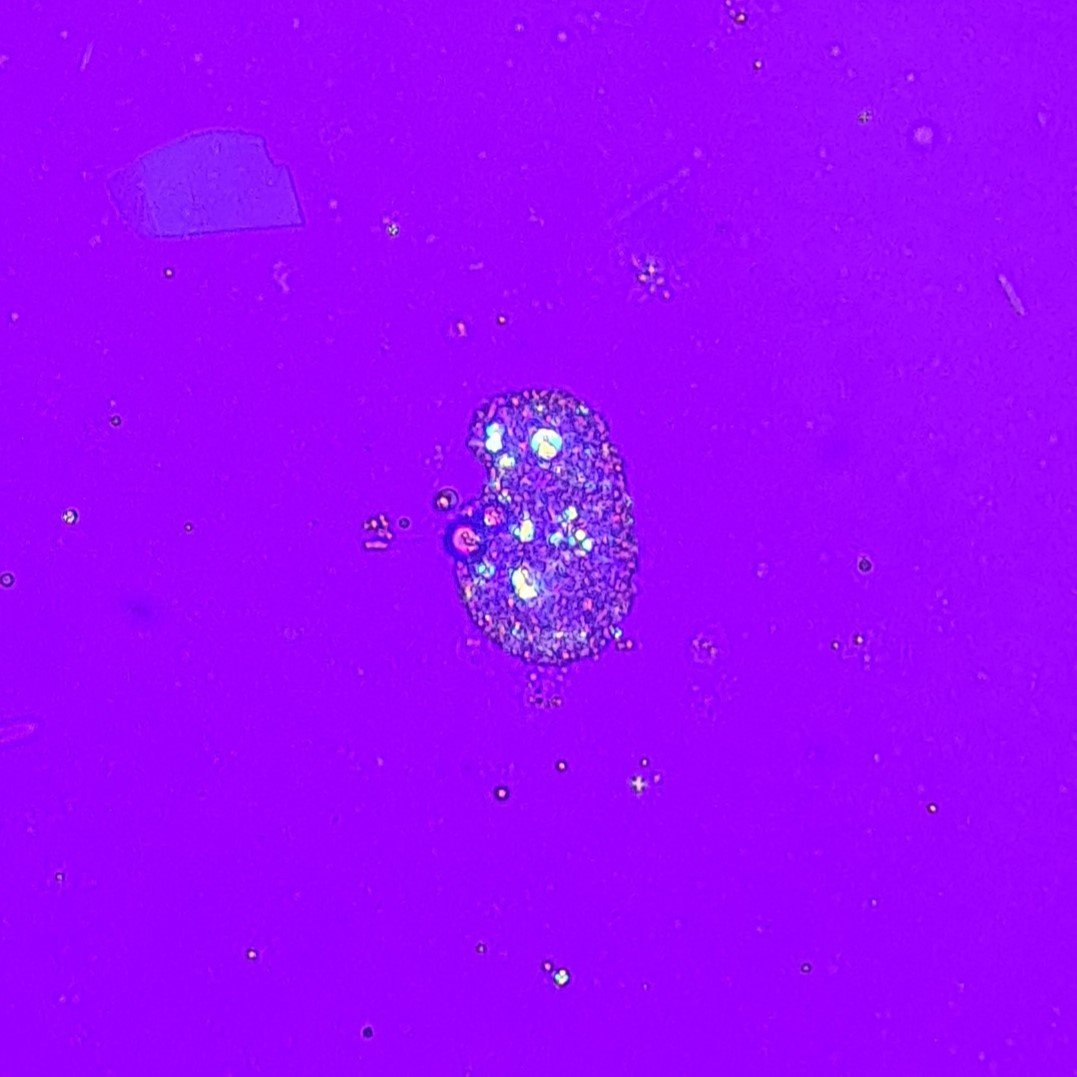
Increased amounts renal tubular epithelial (RTE) cells indicates tubular damage, such as acute tubular necrosis, viral infection, transplant rejection, or drug or heavy metal toxicity.
Appearance
RTEs are slightly larger than a WBC and may be round, oval, or polyhedral. Cytoplasm is finely granular, and nucleus is distinctly round. Difficult to distinguish from transitional epithelial cells.