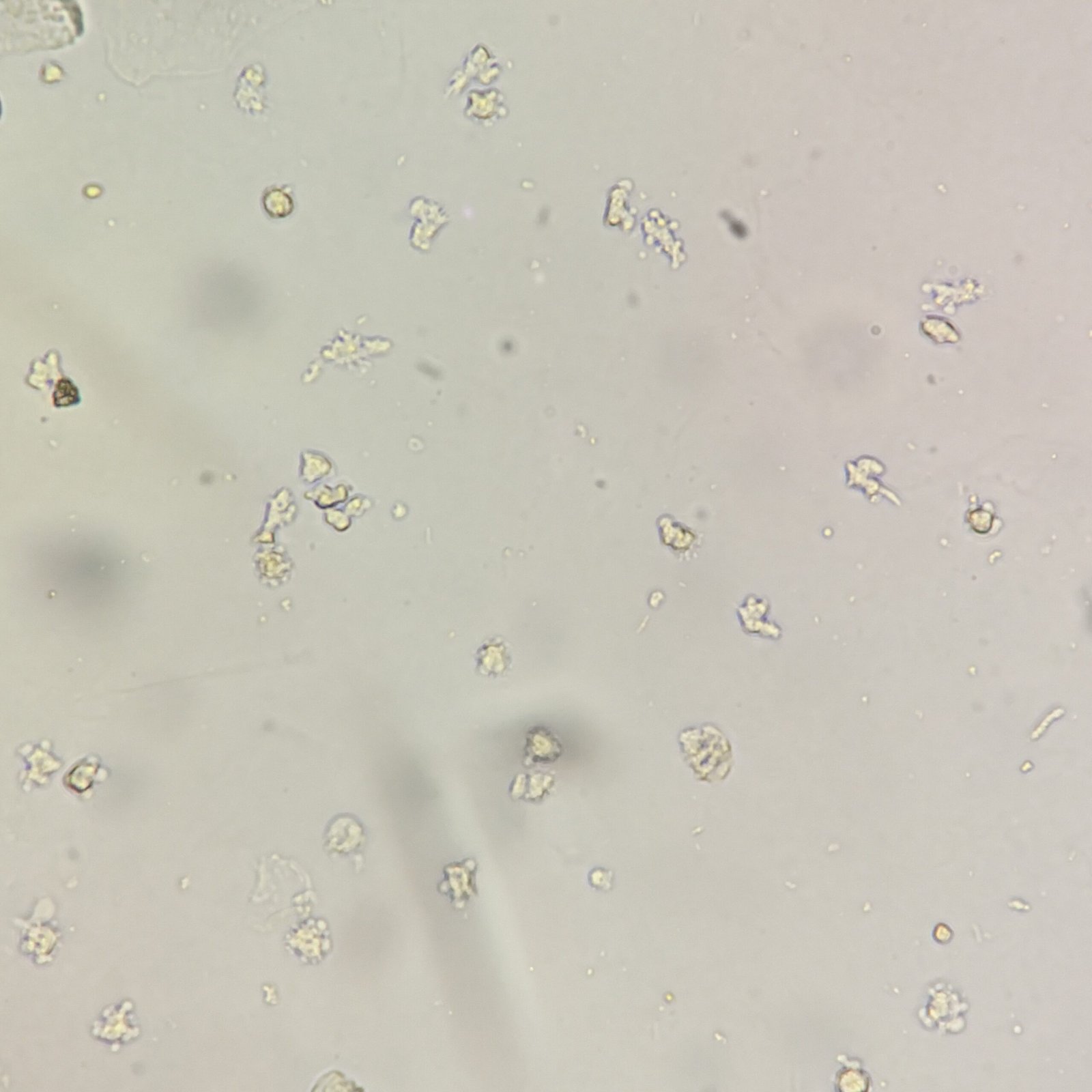
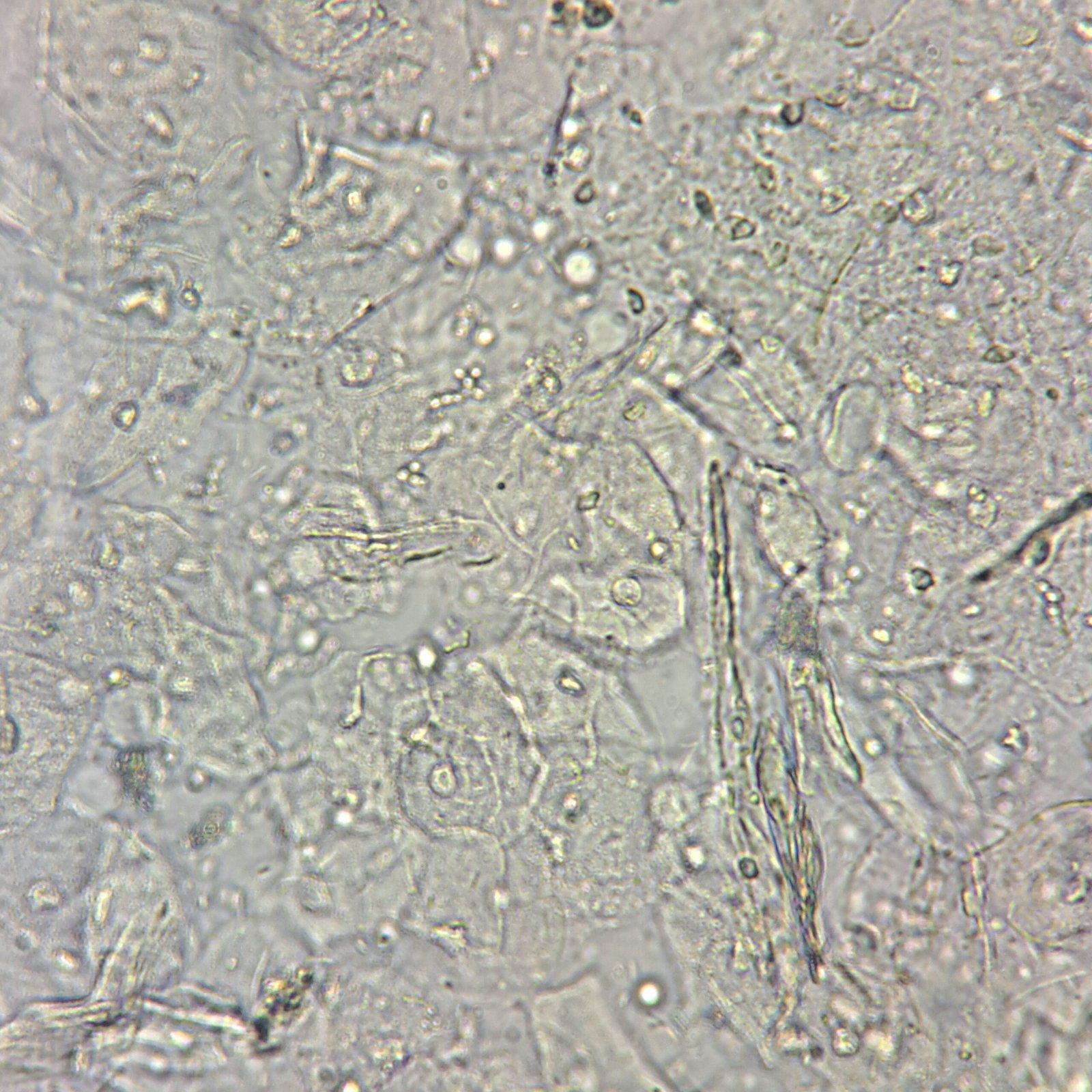
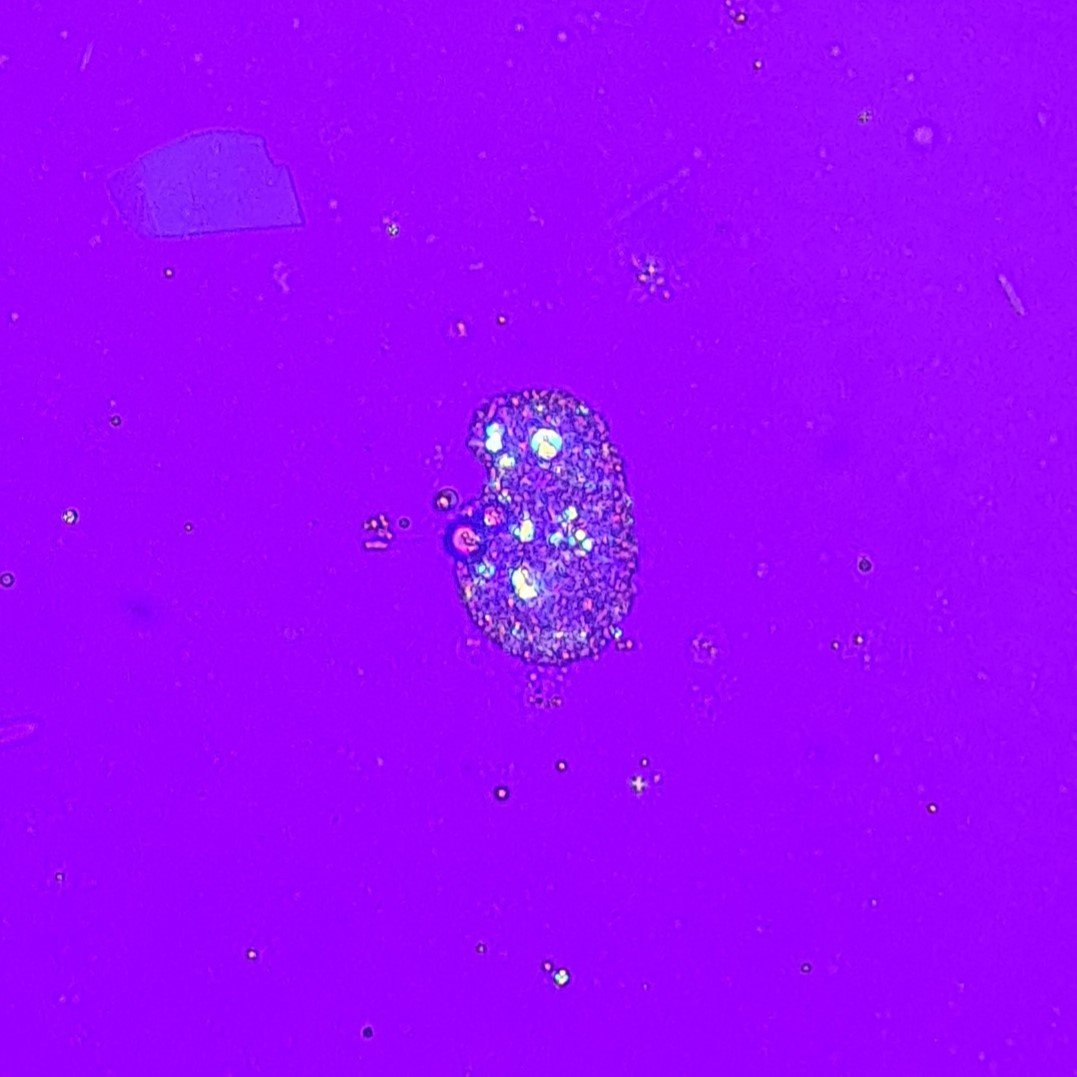
Transitional epithelial cells line the urinary tract from the renal pelvis to the upper portion of the urethra.
Increased amounts of transitional cells may indicate recent catheterization, infection, kidney stones, or bladder cancer.
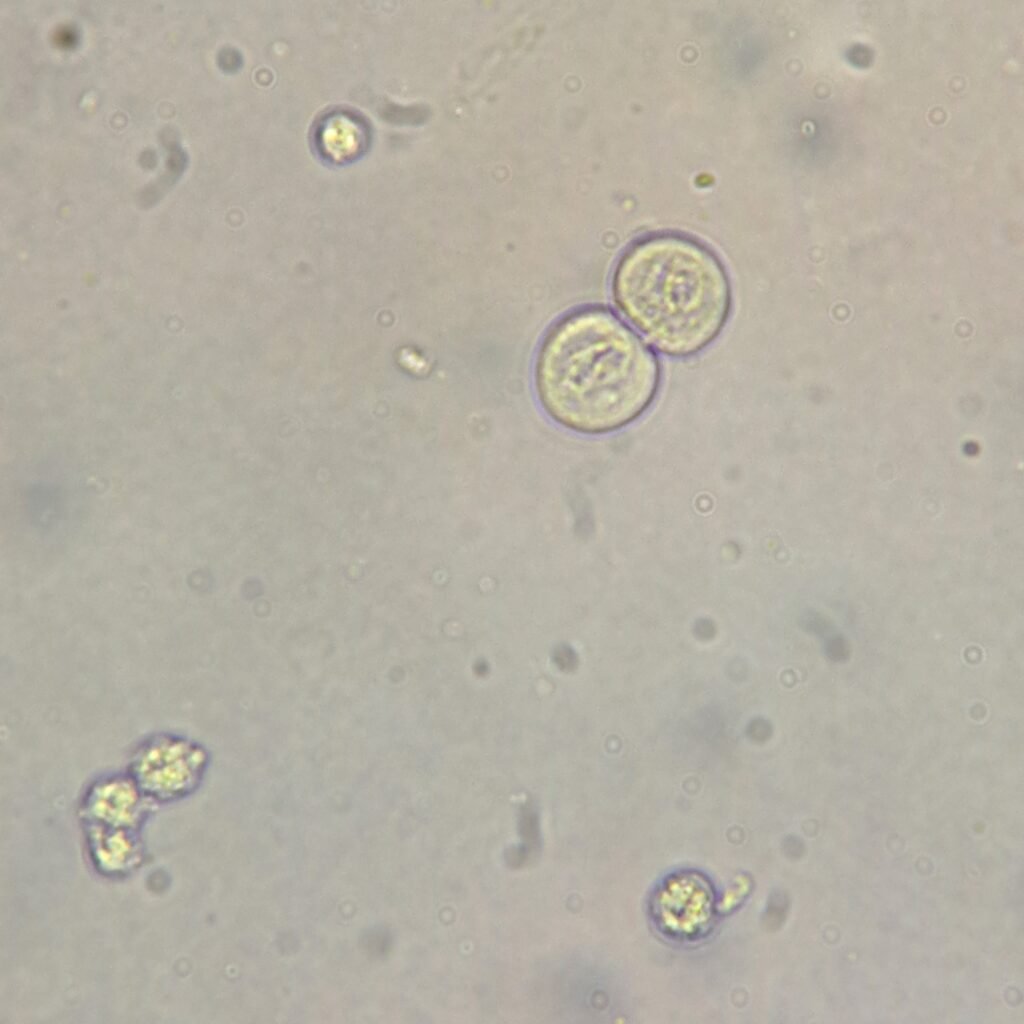
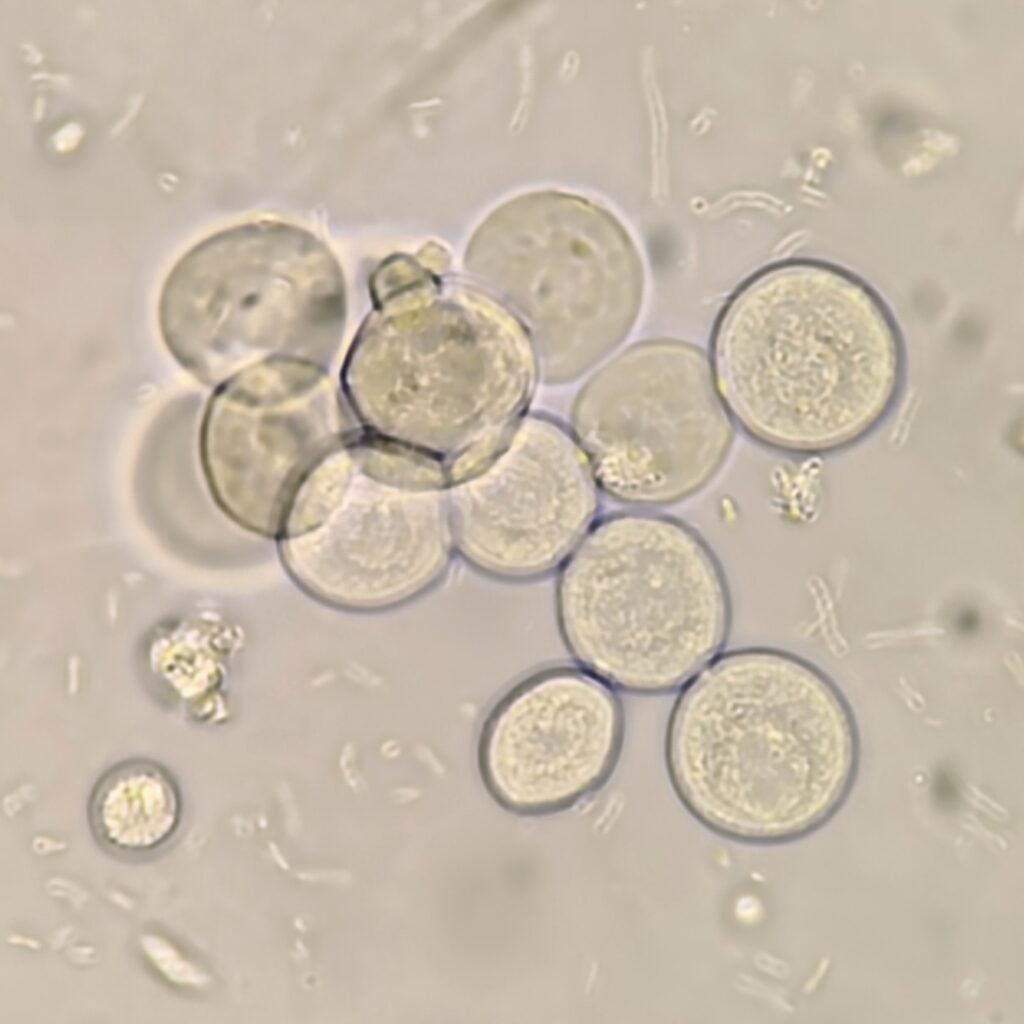
Transitional Cell Appearance
Transitional cells are round or pear-shaped. They have less cytoplasm and a larger nucleus than squamous cells. Their defined border and readiness to absorb water can give them a bubble-like appearance.
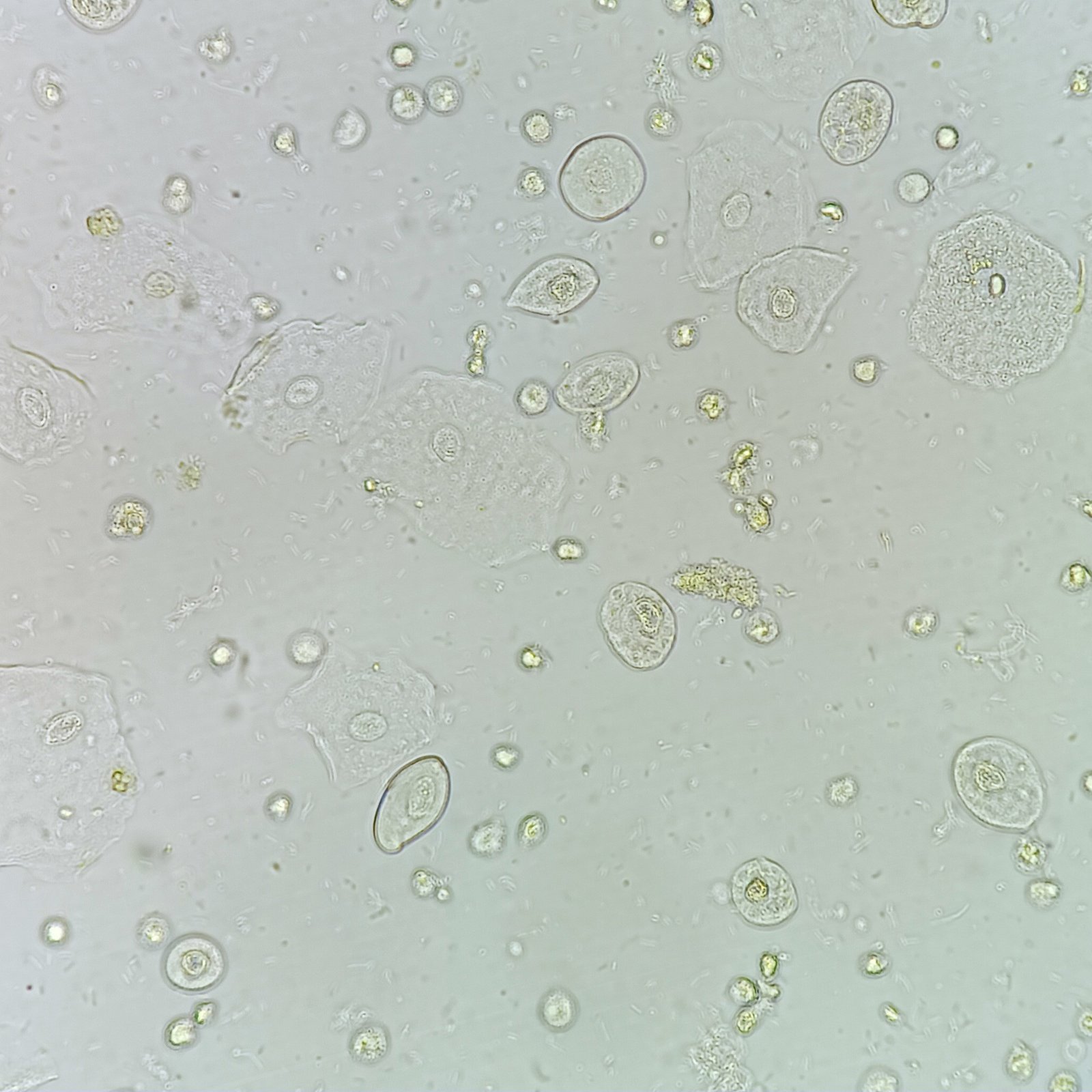
Lookalikes
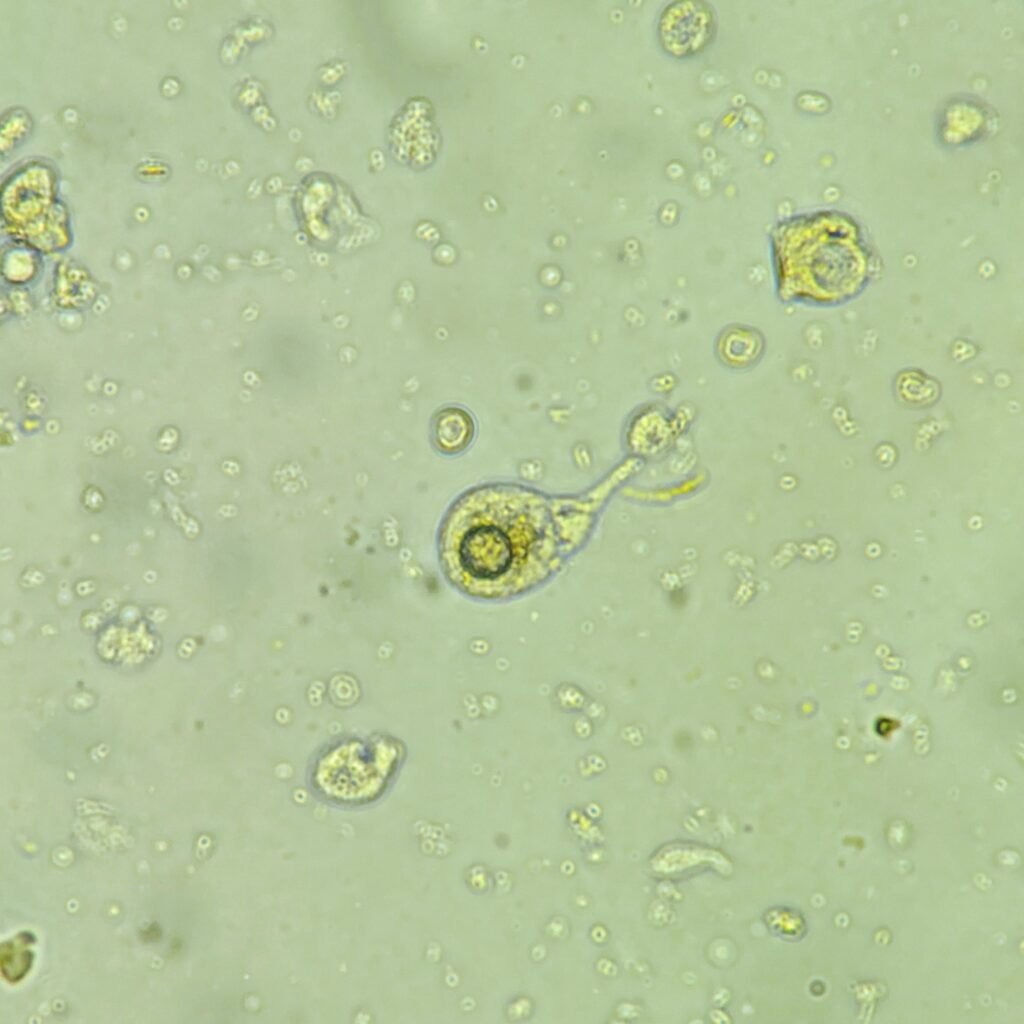
Transitional cells can be mistaken for renal tubular epithelial cells, as the two can look very similar. Renal cells are typically smaller than transitional cells and have fine granules in the cytoplasm. When visual identification is difficult, patient history can help. Recent catheterization for example, makes transitional cells more likely than renal cells.
Gallery